Surface morphology characterization of fixed abrasive lapping pad based on deep learning
-
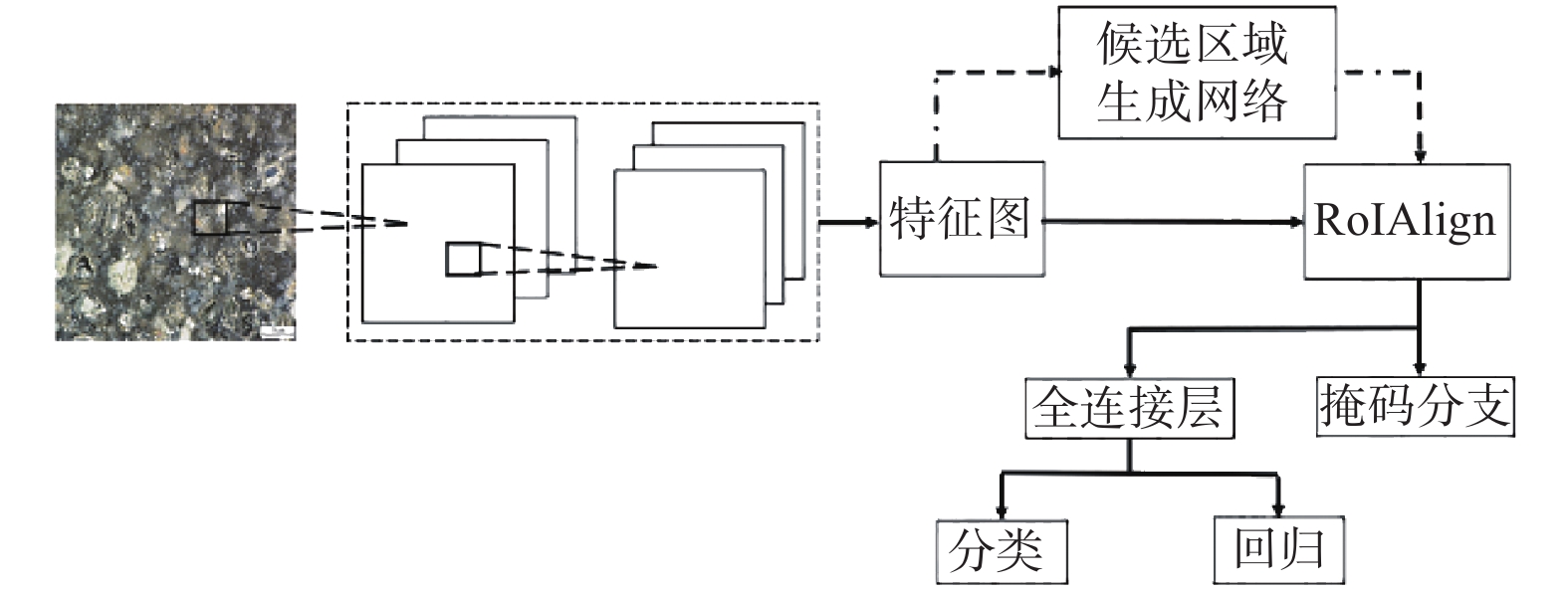
摘要: 固结磨料研磨垫的表面形态与其加工性能有着密切关系,为更好地了解固结磨料研磨垫表面形态,尤其是研磨垫中的金刚石、孔隙、金刚石脱落坑等的分布特征,提出一种基于深度学习的固结磨料研磨垫表面形态分析方法。首先,利用徕卡DVM6数字显微镜及其配套软件获取固结磨料研磨垫表面图像;然后,采用python3+OpenCV对图像进行预处理,并利用标注软件Labelme对图像进行标注,用于后续的训练和测试;最后,运用深度学习框架Tensorflow搭建Mask R-CNN模型。结果表明:Mask R-CNN模型能对单一固结磨料垫表面图像中的多目标进行有效分割与识别,其主要评价指标平均准确率达到78.9%,达到了图像识别的主流水平。Abstract: The surface morphology of fixed abrasive (FA) lapping pad is closely related to its processing performance. In order to understand the surface morphology of the FA lapping pad better, particularly diamonds, pores, and pits resulting from diamond falling off, a deep learning-based method for characterizing its surface morphology was proposed. First, the Leica DVM6 digital microscope and its supporting software were adopted to obtain the surface images of the FA lapping pad; then python3+OpenCV were chosen to preprocess the images, and the labeling software Labelme was used to label the images for subsequent training and testing data set; finally, the Mask R-CNN model was built using the deep learning framework Tensorflow. The results show that the Mask R-CNN model can effectively segment and recognize multiple targets in the surface image of a single fixed abrasive pad, and the average accuracy of the main evaluation indicators reaches 78.9%, reaching the mainstream level of image recognition.
-
Key words:
- fixed abrasive lapping pad /
- deep learning /
- target detection /
- image processing
-
表 1 固结磨料垫磨粒粒径与成孔剂占比
Table 1. Abrasive particle sizes and pore forming agent proportions of FAP
垫子编号 金刚石粒径 d / μm 成孔剂质量分数 ω / % 1 38 30 2 60 30 3 60 40 表 2 类别特征描述
Table 2. Categorical characterization
目标类别 特征描述 金刚石 亮度高,具有折线轮廓 孔隙 亮度低,具有圆弧轮廓 金刚石脱落坑 亮度低,具有折线轮廓 表 3 模型部分超参数
Table 3. Some hyper parameters of the model
参数名称 参数值 类别数 3+1 锚框比例 0.5, 1.0, 2.0 学习率 0.000 1 学习动量 0.9 -
[1] 墨洪磊. 固结磨料研磨垫的制备工艺优化 [D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2013.MO Honglei. Preparation optimization of fixed abrasive pad by thermosetting molding [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2013. [2] 明舜, 李军, 张羽驰, 等. 磨粒尺寸和基体硬度对固结磨料抛光YAG晶体的影响 [J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程,2020,40(3):86-90.MING Shun, LI Jun, ZHANG Yuchi, et al. Effect of abrasive size and matrix hardness on fixed abrasive polishing of YAG crystal [J]. Diamond & Abrasives Engineering,2020,40(3):86-90. [3] 凌顺志, 墨洪磊, 汪忠喜, 等. 磨料尺寸对固结金刚石聚集体磨料垫研磨石英玻璃加工性能的影响 [J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程,2017,37(5):12-18.LING Shunzhi, MO Honglei, WANG Zhongxi, et al. Effect of abrasive sizes on processing characteristics of fixed diamond aggregations pad lapping quartz glass [J]. Diamond & Abrasives Engineering,2017,37(5):12-18. [4] 徐胜. 磨粒改性对固结磨料垫研磨蓝宝石性能的影响 [D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2016.XU Sheng. Effect of abrasive modification on sapphire lapping performance by fixed abrasive pad [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2016. [5] 朱永伟, 王成, 徐俊, 等. 固结磨料研磨垫孔隙结构对其加工性能的影响 [J]. 光学精密工程,2014,266(4):911-917.ZHU Yongwei, WANG Cheng, XU Jun, et al. Influence of pore distribution of fixed abrasive pad on its machining performance [J]. Optics & Precision Engineering,2014,266(4):911-917. [6] 付杰. 固结磨料研磨抛光垫磨粒保持性能研究 [D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2013.FU Jie. Abrasives retaining performance of fixed abrasive pad [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2013. [7] 霍凤伟, 金洙吉, 康仁科, 等. 细粒度金刚石砂轮表面磨粒识别研究 [J]. 大连理工大学学报,2007,47(3):358-362. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-8608.2007.03.010HUO Fengwei, JIN Zhuji, KANG Renke, et al. Recognition of diamond grains on surface of fine diamond grinding wheel [J]. Journal of Dalian University of Technology,2007,47(3):358-362. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-8608.2007.03.010 [8] 贾坡, 田建艳, 杨英波, 等. 基于机器视觉的滚抛磨块缺陷检测方法 [J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程,2021,41(1):76-82.JIA Po, TIAN Jianyan, YANG Yingbo, et al. Defect detection method of abrasive block based on machine vision [J]. Diamond & Abrasives Engineering,2021,41(1):76-82. [9] 赵玉康, 毕文波, 葛培琪. 电镀金刚石线锯表面磨粒分布密度的多相机视觉检测 [J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程,2021,41(2):64-68.ZHAO Yukang, BI Wenbo, GE Peiqi. Multi-camera visual inspection of abrasives distribution density on electroplated diamond wire saw surface [J]. Diamond & Abrasives Engineering,2021,41(2):64-68. [10] 徐杨. 面向视频监控的动态目标检测、跟踪与识别关键技术研究 [D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2012.XU Yang. Research on key technologies of dynamic objects detection, tracking and recognition for video surveillance [D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2012. [11] 杨智宏, 贺石中, 冯伟, 等. 基于Mask R-CNN网络的磨损颗粒智能识别与应用 [J]. 摩擦学学报,2021,41(1):105-114.YANG Zhihong, HE Shizhong, FENG Wei, et al. Intelligent identification of wear particles based on Mask R-CNN network and application [J]. Tribology,2021,41(1):105-114. [12] 肖潇. 基于深度学习的遥感图像处理系统的设计与实现 [D]. 北京: 北京邮电大学, 2019.XIAO Xiao. Design and implementation of remote sensing image processing system based on deep learning [D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2019. [13] 张娟娟, 宋圭辰, 刘斌, 等. 改进的基于Mask R-CNN的碳纤维图像分割方法 [J]. 中国科技论文, 2021, 16(11): 1189-1194, 1208.ZHANG Juanjuan, SONG Guichen, LIU Bin, et al. Improved Mask R-CNN image segmentation method for carbon fiber [J]. China Sciencepaper, 2021, 16(11): 1189-1194, 1208. [14] REN S Q, HE K M, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks [J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence,2017,39(6):1137-1149. [15] 付发, 未建英, 张丽娜. 基于卷积网络的遥感图像建筑物提取技术研究 [J]. 软件工程,2018,21(6):4-7.FU Fa, WEI Jianying, ZHANG Lina. A study of building extraction remote sensing imagery based on convolution network [J]. Software Engineering,2018,21(6):4-7. [16] 安超, 魏海军, 刘竑, 等. 基于Mask R-CNN的铁谱磨粒智能分割与识别 [J]. 润滑与密封,2020,45(3):112-117.AN Chao, WEI Haijun, LIU Hong, et al. Ferrographic wear debris intelligent segmentation and recognition based on Mask R-CNN [J]. Lubrication Engineering,2020,45(3):112-117. [17] 林志洁, 罗壮, 赵磊, 等. 特征金字塔多尺度全卷积目标检测算法 [J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版),2019,53(3):533-540.LIN Zhijie, LUO Zhuang, ZHAO Lei, et al. Multi-scale convolution target detection algorithm with feature pyramid [J]. Journal of Zhejiang University(Engineering Science),2019,53(3):533-540. -





 下载:
下载:







 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS
