On-line identification and monitoring method for external grinding flutter based on BP neural network
-
摘要: 为提高机床磨削加工过程中对颤振现象识别的能力,提出一种基于BP(back propagation)神经网络模型的颤振识别方法。通过对加工过程中传感器采集到的高频声发射信号以及振动信号相关特征值的提取,获得关于颤振的多特征参数样本库,并用其对BP神经网络模型进行学习和训练,建立BP神经网络在线识别颤振的算法模型,实现对机床加工过程中是否发生颤振的在线监测和识别。试验结果表明:这种基于BP神经网络模型的颤振识别测试结果与磨削加工试验中的磨削颤振现象结果相符合。该方法能够有效地识别磨削加工过程中的颤振,并起到在线监测识别的作用。Abstract: To improve the ability of the machine tool to identify chatter during the grinding process, a chatter recognition method is proposed based on the BP (back propagation) neural network model. By extracting the relevant feature values of the high-frequency acoustic emission signals and vibration signals in the processing process, multi-feature signal samples library about flutter are obtained. The multi-feature signal sample library is used to learn and train the BP neural network to establish recognition model. The model realizes on-line monitoring and accurate identification of whether chattering occurring during machine tool processing. The experimental results show that the flutter recognition based on the BP neural network model verifies that the measured test results are consistent with the actual flutter and network recognition results. Therefore, this method can effectively identify the flutter phenomenon in the processing process and play the role of online intelligent monitoring.
-
表 1 时域特征参数计算公式
Table 1. Calculation formula of time domain characteristic parameter
参数 计算公式 参数 计算公式 标准差 $\sigma {\text{ = }}\sqrt {\dfrac{1}{n}\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {{{({x_i} - \bar x)}^2}} } $ 方差 ${\sigma^2} = \dfrac{1}{{n - 1}}\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {{{({x_i} - \bar x)}^2}} $ 极差 $R = {x_{\max }} - {x_{\min }}$ 均方根 ${X_{RMS}} = \sqrt {\left(\dfrac{1}{n}\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {x_i^2} \right)} $ 均值 $\bar x = \dfrac{1}{n}\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {{x_i}} $ 偏态系数 $C_{\rm s} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{1}{n}\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {{{({x_i} - \bar x)}^3}} }}{{{{\left(\dfrac{1}{n}\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {{{({x_i} - \bar x)}^2}} \right)}^{\textstyle\frac{3}{2}}}}}$ 峰值 ${X_{\text{p}}} = \max \left| {x(n)} \right|$ 峰值
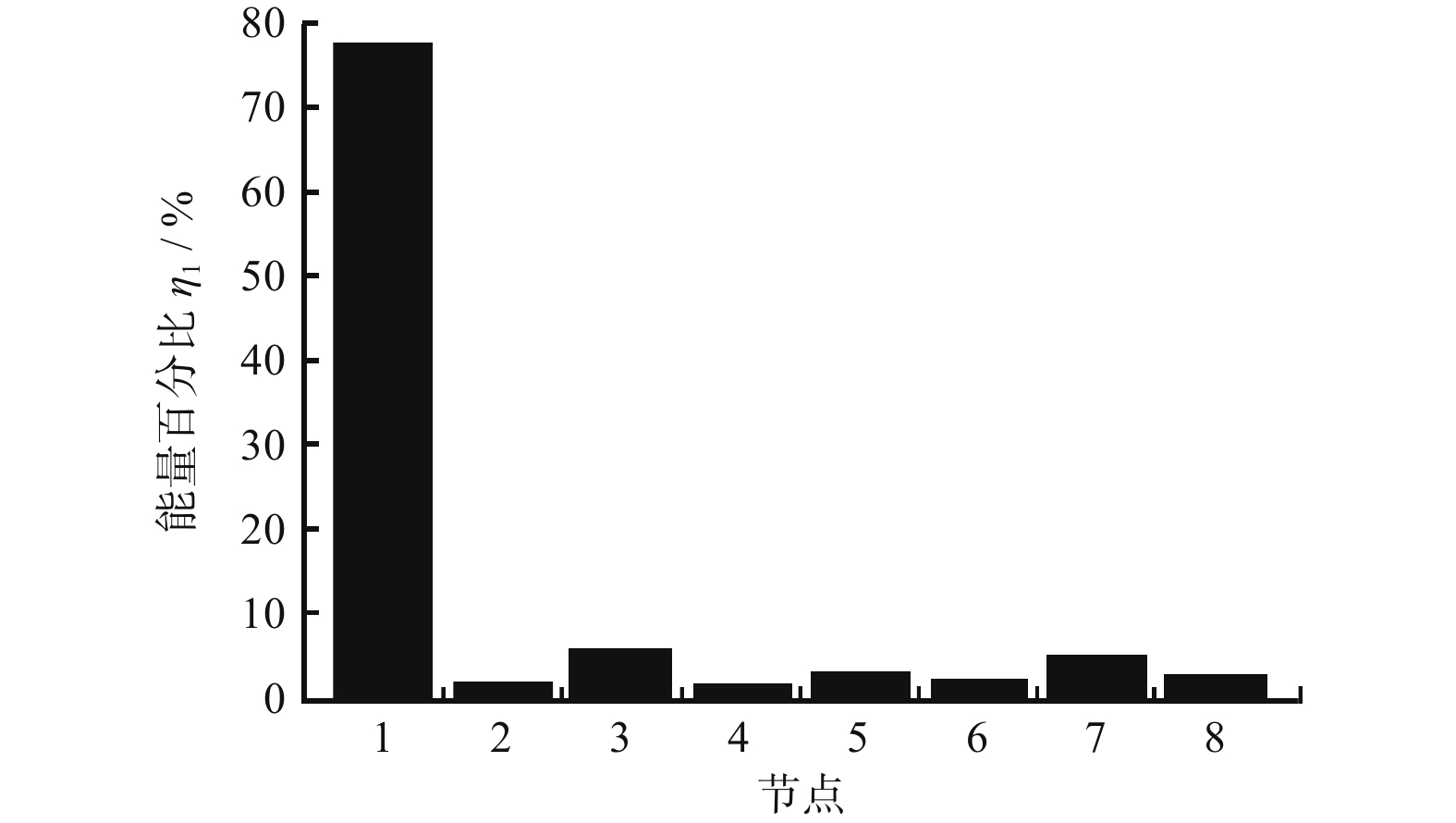
因子$C = \dfrac{{{X_P}}}{{\sqrt {\left(\dfrac{1}{n}\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {x_i^2} \right)} }}$ 表 2 工件磨削AE频谱能量分布占比
Table 2. AE spectrum energy distribution occupation of workpiece grinding
节点 低速时能量占比 η1 / % 高速时能量占比 η2 / % 1 77.127 7 36.612 5 2 2.842 3 27.440 2 3 5.690 3 9.365 1 4 1.766 0 4.963 5 5 2.751 3 4.787 6 6 2.292 2 3.981 8 7 5.201 5 8.793 2 8 2.328 7 4.056 1 表 3 高频声发射小波包能量占比(高速)
Table 3. High frequency acoustic emission wavelet packet energy ratio (high speed)
序号能量占比 η3 / %
现象节点1 节点2 节点3 1 36.6 22.0 10.5 有颤振 2 34.3 21.9 11.1 有颤振 3 30.9 13.8 14.7 有颤振 ··· ··· ··· ··· ··· 78 36.1 21.9 10.3 有颤振 79 35.3 21.8 10.5 有颤振 80 29.7 14.3 14.3 有颤振 表 4 高频声发射小波包能量占比(低速)
Table 4. High frequency acoustic emission wavelet packet energy ratio (high speed)
序号能量占比 η4 / %
现象节点1 节点2 节点3 1 78.5 1.78 5.33 无颤振 2 78.0 2.00 5.40 无颤振 3 78.5 1.81 5.30 无颤振 ··· ··· ··· ··· ··· 78 78.2 1.57 5.47 无颤振 79 78.0 1.65 5.55 无颤振 80 77.7 1.87 5.56 无颤振 表 5 三向振动信号特征值提取
Table 5. Eigenvalue extraction of three-way vibration signal
序号 x轴振动信号
均方根XRMSy轴振动信号
偏态系数$Cs$z轴振动信号
标准差$\sigma $现象 1 0.022 8 0.005 6 0.021 6 有颤振 2 0.021 4 0.030 5 0.017 3 有颤振 3 0.019 6 −0.082 7 0.014 9 有颤振 ··· ··· ··· ··· ··· 158 0.141 8 0.035 9 0.012 1 无颤振 159 0.141 7 0.087 0 0.011 7 无颤振 160 0.141 8 −0.011 0 0.011 8 无颤振 表 6 预测结果数据
Table 6. Forecast result data
序号 真实值 预测值 算法误差 现象 预测结果 1 2.000 0 1.991 5 0.42% 无颤振 正确 2 1.000 0 1.001 2 0.12% 有颤振 正确 3 2.000 0 1.992 8 0.36% 无颤振 正确 4 1.000 0 1.008 0 0.80% 有颤振 正确 5 2.000 0 1.992 3 0.39% 无颤振 正确 6 1.000 0 0.994 6 0.54% 有颤振 正确 7 1.000 0 1.005 4 0.54% 有颤振 正确 8 2.000 0 1.992 6 0.37% 无颤振 正确 9 2.000 0 1.982 9 0.85% 无颤振 正确 10 2.000 0 1.990 5 0.47% 无颤振 正确 -
[1] MUNOA J, BEUDAERT X, DOMBOVVARIZ, et al. Chatter suppression techniques in metal cutting [J]. CIRP Annals-Manufacturing Technology,2016,65(2):785-808. doi: 10.1016/j.cirp.2016.06.004 [2] 江卓达, 何永义. 磨削颤振特性研究进展 [J]. 制造技术与机床, 2012(9): 35-42.JIANG Zhuoda, HE YongYi. Advances of research on the character of grinding chatter [J]. Manufacturing Technology and Machine Tools, 2012(9): 35-42. [3] 于骏一, 周晓勤. 切削颤振的预报控制 [J]. 中国机械工程, 1999, 10(9): 1028-1032.YU Junyi, ZHOU Xiaoqin. Predictive control of cutting chatter [J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 1999, 10(9): 1028-1032. [4] 孔繁森, 于骏一, 勾治践. 颤振状态的模糊识别 [J]. 振动工程学报, 1998(3): 81-85.KONG Fansen, YU Junyi, GOU Zhijian. Fuzzy identification of flutter state [J]. Journal of Vibration Engineering, 1998(3): 81-85. [5] 钱士才, 孙宇昕, 熊振华. 基于支持向量机的颤振在线智能检测 [J]. 机械工程学报, 2015(20): 1-8.QIAN Shicai, SUN Yuxin, XIONG Zhenhua. Support vector machine based online intelligent chatter detection [J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2015(20): 1-8. [6] 吕长飞, 吴小玉, 王茵, 等. 外圆磨削颤振监测方法设计 [J]. 机床与液压, 2019, 47(8): 166-168, 66.LYU Changfei, WU Xiaoyu, WANG Yin, et al. Design of chatter detection in external cylindrical grinding [J]. Machine Tools and Hydraulics, 2019, 47(8): 166-168, 66. [7] KULJANIC E, TOTIS G, SORTINO M. Development of an intelligent multisensor chatter detection system in milling [J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing,2009,23(5):1704-1718. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2009.01.003 [8] 黄强, 张根保, 张新玉. 对再生型切削颤振模型的试验分析 [J]. 振动工程学报, 2008, 21(6): 547-552.HUANG Qiang, ZHANG Genbao, ZHANG Xinyu. Experimental analysis on regenerative chatter model [J]. Journal of Vibration Engineering, 2008, 21(6): 547-552. [9] 王海龙. 机床颤振分析及抑制方法研究 [D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2013.WANG Hailong. Research on chatter analysis and suppression method of machine tool [D]. Harbin: Harbin Engineering University, 2013. [10] 李泽阳, 郑飂默, 李备备, 等. 基于改进BP神经网络的机床温度预警 [J]. 组合机床与自动化加工技术, 2021(9): 81-84, 89.LI Zeyang, ZHENG Liaomo, LI Beibe, et al. Temperature warning of machine tool based on improved BP neural network [J]. Modular Machine Tool and Automatic Machining Technology, 22021(9): 81-84, 89. [11] 谢峰云, 曹青松, 黄志刚. 基于小波包-BP神经网络的切削颤振监测 [J]. 仪表仪器与传感器, 2015(10): 88-90.XIE Fengyun, CAO Qingsong, HUANG Zhigang. Chatter monitoring based on wavelet packet and BP neural network [J]. Instruments and Sensors, 2015(10): 88-90. [12] 张强, 刘志恒, 王海舰, 等. 基于BP神经网络的截齿磨损程度在线监测 [J]. 中国机械工程, 2017, 28(9): 1062-1068.ZHANG Qiang, LIU Zhiheng, WANG Haijian, et al. On-line monitoring of pick’s wear degrees based on BP neural network [J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2017, 28(9): 1062-1068. [13] 侯智, 曾杰. 基于BP神经网络的轴承套圈沟道磨削粗糙度识别 [J]. 机械设计与研究, 2019, 35(3): 119-122.HOU Zhi, ZENG Jie. Roughness identification of bearing ring groove grinding based on bp neural network [J]. Mechanical Design and Research, 2019, 35(3): 119-122. [14] 谢锋云, 江炜文, 陈红年, 等. 基于广义BP神经网络的切削颤振识别研究 [J]. 振动与冲击, 2018, 37(5): 65-70, 78.XIE Fengyun, JIANG Weiwen, CHEN Hongnian, et al. Cutting chatter recognition based on generalized BP neural network [J]. Vibration and Shock, 2018, 37(5): 65-70, 78. -





 下载:
下载:








 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS
