Flatness prediction of single pendulum polishing based on microelement material removal model
-
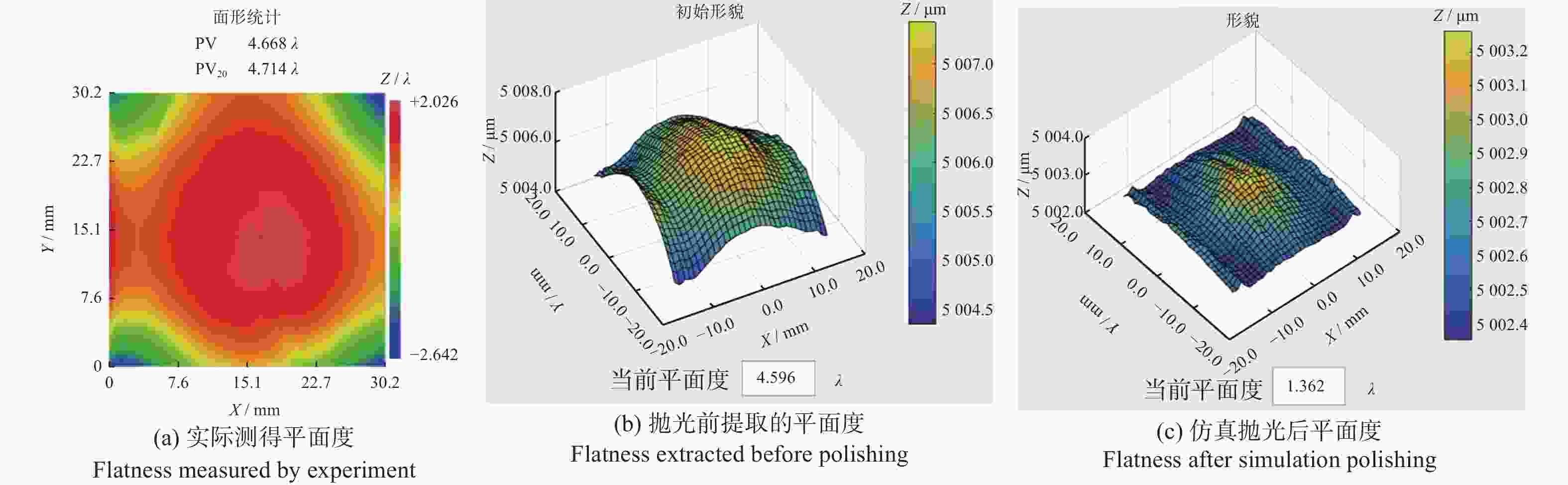
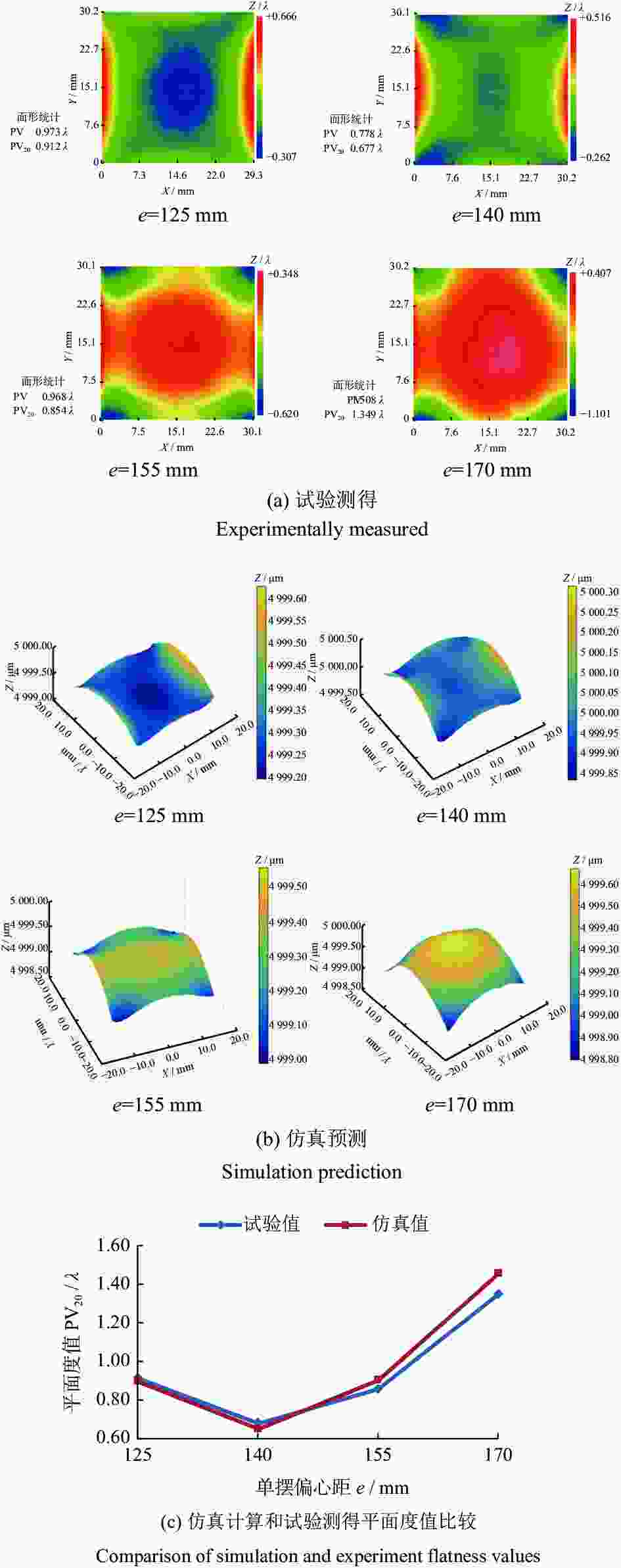
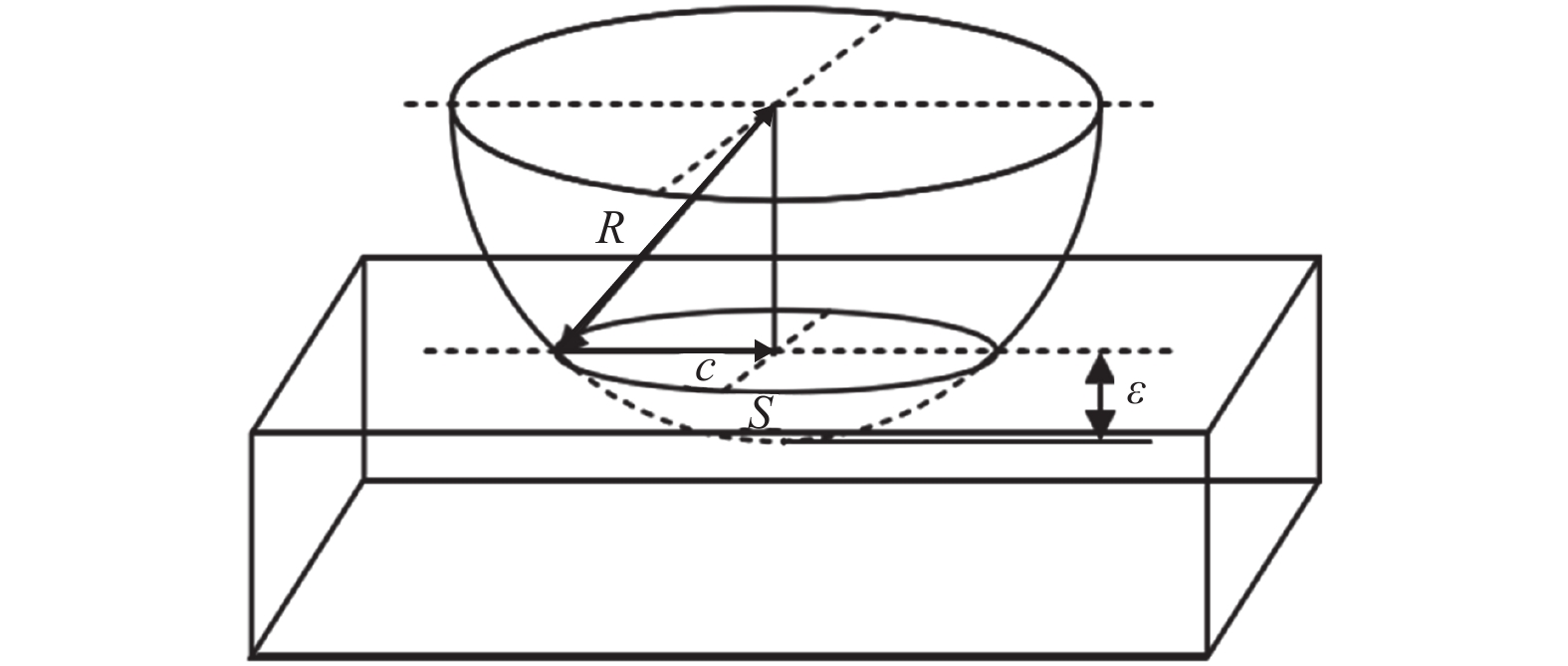
摘要: 为探究单摆参数对抛光工件平面度的影响,提出一种基于速度和压强分布耦合的抛光微元材料去除模型,以预测工件表面平面度。从单颗磨粒的材料去除出发,建立工件表面各微元单位时间内材料去除厚度模型,并将工件相对抛光垫速度和工件表面压强分布耦合代入模型;根据工件初始面形提取微元高度值,结合各微元材料去除的厚度,计算抛光后的工件表面平面度;试验验证平面度预测方法。结果表明:仿真与实际抛光后的面形的变化趋势相同,平面度PV20值绝对偏差小于12.0%,平面度预测可靠。Abstract: A microelement material removal model was proposed to explore the influence of single pendulum parameters on the polishing flatness of workpiece. Based on the coupling of velocity and pressure distribution, the model could predict the polishing flatness. Starting from the material removal of single abrasive particle, the model of material removal height of each microelement on the workpiece surface in unit time was established. The velocity of workpiece relative to polishing pad and pressure distribution of workpiece surface was coupled and inserted into the model. According to the initial surface shape of workpiece, the height value of microelement was extracted, and the flatness of the workpiece after polishing was calculated combined with the thickness of microelement material removal. Experiments were carried out to validate the flatness prediction method. The results show that the change trend of the surface shape after simulated polishing is same as actual polishing, and the absolute deviation of flatness PV20 is less than 12.0%. The flatness prediction is reliable.
-
表 1 平面度预测工艺参数
Table 1. Process parameters of flatness prediction
参数 数值 单摆幅度2θ / (°) 30 单摆偏心距 e / mm 160 单摆偏置角度 φ / (°) 0 抛光垫转速 ω1 / (r·min−1) 25 工件转速 ω2 / (r·min−1) 30 单摆频率 f / (n·min−1) 11 中心加压压强 p / kPa 15 抛光时间 t / min 5 表 2 验证平面度变化试验的抛光参数
Table 2. Polishing parameters of proving flatness change test
抛光参数 组1 组2 组3 单摆偏心距 e / mm 125,140,
155,170155 145 单摆幅
度2θ / (°)25 15,20,
25,3015 单摆偏置角度 φ / (°) 0 0 0,4,
8,12表 3 验证平面度变化试验的其他抛光参数
Table 3. Other polishing parameters of proving flatness change test
参数 数值 抛光垫转速 ω1 / (r·min−1) 20 工件转速 ω2 / (r·min−1) 25 单摆频率 f / (n·min−1) 10 中心加压压强 p / kPa 11 抛光时间 t / min 10 -
[1] ZHAO G Y, WEI Z, WANG W L, et al. Review on modeling and application of chemical mechanical polishing [J]. Nanotechnology Reviews,2020,9(1):182-189. doi: 10.1515/ntrev-2020-0016 [2] 郭东明, 康仁科, 苏建修, 等. 超大规模集成电路制造中硅片平坦化技术的未来发展 [J]. 机械工程学报,2003,39(10):100-105. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0577-6686.2003.10.017GUO Dongming, KANG Renke, SU Jianxiu, et al. Future development on wafer planarization technology in VLSI fabrication [J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2003,39(10):100-105. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0577-6686.2003.10.017 [3] 尹进, 朱健强, 焦翔, 等. 基于环形抛光的稳态确定性抛光方法 [J]. 中国激光,2017,44(11):42-50.YIN Jin, ZHU Jianqiang, JIAO Xiang, et al. Method of steady-state deterministic polishing based on continuous polishing [J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers,2017,44(11):42-50. [4] 万策, 金洙吉, 吴頔, 等. 大径厚比铜片的化学机械抛光 [J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程,2018,38(3):81-85.WAN Ce, JIN Zhuji, WU Di, et al. Chemical mechanical planarization of copper sheet with high radius-thickness ratio [J]. Diamond & Abrasives Engineering,2018,38(3):81-85. [5] ZHONG G H, NING Y D, ZHOU Q G, et al. Influence of pre-polishing process on site flatness values of polished wafers [J]. Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing,2017,68(9):15-20. [6] PAN B, KANG R K, GUO J, et al. Precision fabrication of thin copper substrate by double-sided lapping and chemical mechanical polishing [J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes,2019,44(6):47-54. [7] SUZUKI N, HASHIMOTO Y, YASUDA H, et al. Prediction of polishing pressure distribution in CMP process with airbag type wafer carrier [J]. CIRP Annals-Manufacturing Technology,2017,66(1):329-332. doi: 10.1016/j.cirp.2017.04.088 [8] PARK C, JEONG H, LEE S. A study on pressure distribution for uniform polishing of sapphire substrate [J]. Tribology and Lubricants,2016,32(2):61-66. [9] LI J, WEI Z H, WANG T Q, et al. A theoretical model incorporating both the nano-scale material removal and wafer global uniformity during planarization process [J]. Thin Solid Films,2017,636(8):240-246. [10] ZHAO C, LI J, YI D, et al. Wafer flatness modeling in chemical mechanical polishing [J]. Journal of Electronic Materials,2020,49(1):353-363. doi: 10.1007/s11664-019-07799-y [11] 李鑫, 梁庭, 赵丹, 等. 蓝宝石化学机械抛光时磨粒运动轨迹及抛光效果研究 [J]. 润滑与密封,2018,43(4):57-63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-0150.2018.04.011LI Xin, LIANG Ting, ZHAO Dan, et al. Trajectory of abrasive particles and effect of polishing in chemical mechanical polishing of sapphire [J]. Lubrication Engineering,2018,43(4):57-63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-0150.2018.04.011 [12] 严振, 方从富, 刘冲. 偏摆式平面研磨抛光轨迹的理论研究 [J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程,2018,38(4):77-82.YAN Zhen, FANG Congfu, LIU Chong. Theoretical study on trajectory of swinging plane lapping and polishing [J]. Diamond & Abrasives Engineering,2018,38(4):77-82. [13] 唐咏凯, 李军, 花成旭, 等. 抛光垫磨损非均匀性研究 [J]. 光学技术,2017,43(3):222-227.TANG Yongkai, LI Jun, HUA Chengxu, et al. Research on wear nonuniformity of polishing pad [J]. Optical Technique,2017,43(3):222-227. [14] 王建彬. 固结磨料研磨蓝宝石工件的材料去除机理及工艺研究 [D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2015.WANG Jianbin. Material removal mechanism and process research of lapping sapphire by fixed abrasive [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2015. [15] ZHAO Y W, CHANG L. A micro-contact and wear model for chemical-mechanical polishing of silicon wafers [J]. Wear,2002,252(3/4):220-226. [16] 王旭, 张学军. 固着磨料加工碳化硅反射镜的微观理论模型 [J]. 光学精密工程,2009,17(3):513-518. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-924X.2009.03.008WANG Xu, ZHANG Xuejun. Micro theoretical model for grinding SiC mirror with fixed abrasive [J]. Optics and Precision Engineering,2009,17(3):513-518. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-924X.2009.03.008 [17] JOHNSON K. 接触力学 [M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 1992.JOHNSON K. Contact mechanics [M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 1992. -





 下载:
下载:







 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS
