Research on grinding quality and removal mechanism of polycrystalline diamond tools
-
摘要: 针对聚晶金刚石(PCD)刀具的研磨质量问题,选择刃口钝圆半径、刃口缺陷度、后刀面粗糙度作为评价指标进行工艺参数的优化试验,并分析PCD的研磨去除机理。结果表明:工作台调定压力对刃口钝圆半径影响最显著;金刚石砂轮对刃口缺陷度影响最显著;砂轮转速对后刀面粗糙度影响最显著。选择4/5陶瓷基金刚石砂轮、1 000 r/min砂轮转速、170 N工作台调定压力可以获得研磨质量较高的PCD刀具。试验条件下,PCD的主要去除方式为划擦作用与微细破碎。1 000 r/min砂轮转速、170 N工作台调定压力下的微细破碎在保证较小刃口钝圆半径与刃口缺陷度的同时,可以获得相对平整的PCD表面。Abstract: Aiming at grinding quality of polycrystalline diamond (PCD) tools, the grinding experiment was carried out to optimize the process parameters with cutting edge radius, cutting edge defect and flank roughness as the indexes. The grinding removal mechanism of PCD was also studied. The results show that the worktable setting pressure has the most significant effect on cutting edge radius. The diamond grinding wheel has the most significant effect on cutting edge defect. The grinding wheel speed has the most significant effect on flank roughness. PCD tools with high grinding quality can be obtained by using 4/5 ceramic-based diamond grinding wheel, 1 000 r/min grinding wheel speed and 170 N worktable setting pressure. Under the experimental conditions, the main removal methods of PCD are sliding effect and micro cracking. Smaller cutting edge radius, cutting edge defect and smoother surface of PCD can be obtained by micro cracking under the 1 000 r/min grinding wheel speed and the 170 N worktable setting pressure.
-
Key words:
- PCD tools /
- orthogonal test /
- parameter optimization /
- grinding removal mechanism
-
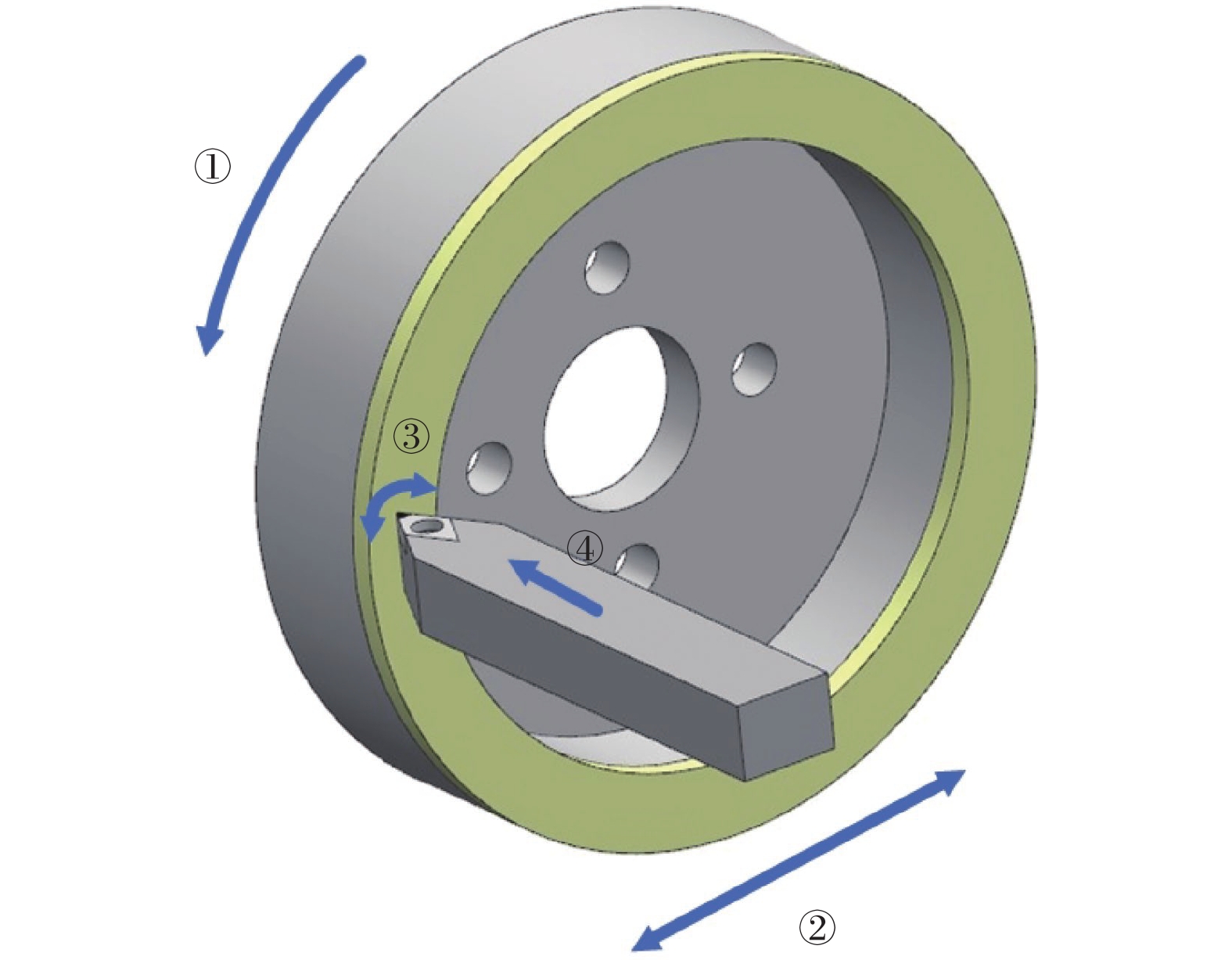
表 1 PCD刀具研磨工艺正交试验
Table 1. Orthogonal test of PCD tool grinding process
水平 A
金刚石砂轮
B
砂轮转速
n / (r·min−1)C
工作台调定压力
F / N1 4/5陶瓷基 800 70 2 6/8金属基 1 000 170 3 6/8金属基
(拟水平)1 200 270 表 2 PCD刀具研磨工艺正交试验结果
Table 2. Orthogonal test results of PCD tool grinding process
试验号 A B C 刃口钝圆半径 ${\gamma _{\text{β }}}$ / μm 刃口缺陷度 $\Delta r$ / μm 后刀面粗糙度 Sa / μm 1 4/5陶瓷基 800 70 7.5 6.5 0.056 2 4/5陶瓷基 1 000 170 7.6 6.1 0.039 3 4/5陶瓷基 1 200 270 7.9 7.2 0.054 4 6/8金属基 800 170 7.4 9.4 0.060 5 6/8金属基 1 000 270 7.8 8.9 0.046 6 6/8金属基 1 200 70 8.2 9.3 0.068 7 6/8金属基 800 270 8.9 9.4 0.052 8 6/8金属基 1 000 70 8.1 8.3 0.051 9 6/8金属基 1 200 170 7.3 7.9 0.051 表 3 极差分析结果
Table 3. Range analysis results
优化指标 水平 因素在各水平下均值 A B C 刃口钝圆半径 ${\gamma _{\text{β }}}$ / μm 1 7.7 7.9 7.9 2 8.0 7.8 7.4 3 7.8 8.2 极差 0.3 0.1 0.8 刃口缺陷度 $\Delta r$ / μm 1 6.6 8.4 8.0 2 8.9 7.8 7.8 3 8.1 8.5 极差 2.3 0.6 0.7 后刀面粗糙度 Sa / μm 1 0.050 0.056 0.051 2 0.055 0.048 0.052 3 0.058 0.056 极差 0.005 0.013 0.005 -
[1] 关佳亮, 任勇, 赵显辉, 等. 聚晶金刚石复合片镜面加工工艺优化研究 [J]. 现代制造工程,2018(1):6-10.GUAN Jialiang, REN Yong, ZHAO Xianhui, et al. Research on mirror finishing optimization process of polycrystalline diamond compact [J]. Modern Manufacturing Engineering,2018(1):6-10. [2] 何云, 杨泊莘, 高阳华, 等. 聚晶金刚石刀具的制造及应用 [J]. 工具技术,2018,52(11):53-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7008.2018.11.025HE Yun, YANG Boxin, GAO Yanghua, et al. Manufacture and application of PCD tool [J]. Tool Engineering,2018,52(11):53-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7008.2018.11.025 [3] LI G, RAHIM M Z, PAN W, et al. The manufacturing and the application of polycrystalline diamond tools – A comprehensive review [J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes,2020,56(5):400-416. [4] ENESCU I. Research in the field of polycrystalline diamond tools [J]. International Journal of Energy and Environment,2020,14(4):14-18. [5] 邓福铭, 张黎燕, 邓雯丽, 等. 聚晶金刚石表面加工质量对比试验研究 [J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程,2019,39(5):33-38.DENG Fuming, ZHANG Liyan, DENG Wenli, et al. Comparative experimental study of machining quality of polycrystalline diamond [J]. Diamond & Abrasives Engineering,2019,39(5):33-38. [6] ZHANG Z Y, DENG Z P, LONG J, et al. The research of PCD tool sharpening process parameters based on uniform design [J]. International Conference on Logistics Engineering, Management and Computer Science,2014,14:623-627. [7] BERGS T, MÜLLER U, VITS F, et al. Grinding wheel wear and material removal mechanisms during grinding of polycrystalline diamond [J]. Procedia CIRP,2020,93:1520-1525. doi: 10.1016/j.procir.2020.03.083 [8] 贾乾忠. 聚晶金刚石刀具关键制作工艺及机理研究 [D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2015.JIA Qianzhong. Research on key manufacturing technology and mechanism of polycrystalline diamond cutting tool [D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2015 [9] 师润平, 韩春钰. PCD刀具刃磨质量研究 [J]. 制造技术与机床,2017(8):87-91.SHI Runping, HAN Chunyu. Study on the grinding quality of PCD cutting tool [J]. Manufacturing Technology & Machine Tool,2017(8):87-91. [10] 李超国. 微圆弧金刚石刀具质量的测量与评价技术 [D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2021.LI Chaoguo. Measurement and evaluation of micro diamond cutting tool [D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2021. [11] 李嫚, 贾乾忠, 张弘弢, 等. 基于表面微观形貌的聚晶金刚石脆性去除机理研究 [J]. 机械工程学报,2014,50(13):202-206. doi: 10.3901/JME.2014.13.202LI Man, JIA Qianzhong, ZHANG Hongtao, et al. Study on brittle removal mechanism of polycrystalline diamond based on surface micro-morphology [J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2014,50(13):202-206. doi: 10.3901/JME.2014.13.202 [12] 贾乾忠, 李嫚, 张弘弢, 等. 聚晶金刚石复合片非脆性去除磨削机理研究 [J]. 大连理工大学学报,2015,55(3):281-285. doi: 10.7511/dllgxb201503008JIA Qianzhong, LI Man, ZHANG Hongtao, et al. Study on non brittle removal grinding mechanism of polycrystalline diamond composite [J]. Journal of Dalian University of Technology,2015,55(3):281-285. doi: 10.7511/dllgxb201503008 [13] WALMSLEY J C, LANG A R. Characteristics of diamond regrowth in a synthetic diamond compact [J]. Journal of Materials Science,1988,23(5):1829-1834. doi: 10.1007/BF01115728 [14] 王适, 张弘弢. 聚晶金刚石热稳定性的研究 [J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报,2005,37(3):408-411. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0367-6234.2005.03.035WANG Shi, ZHANG Hongtao. Study on thermal stability of polycrystalline diamond compacts [J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology,2005,37(3):408-411. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0367-6234.2005.03.035 -





 下载:
下载:












 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS
