Research on abrasive wear dress of CBN honing tool based on single abrasive cutting
-
摘要: 采用单颗磨粒试验方法,以4Cr13不锈钢为修整材料,研究大长径比CBN铰珩工具修整过程中的磨粒磨损特性。试验结果显示:与普通切削相比,超声切削时的平均切削力降低60%~80%,但磨粒在短时间内大块破碎,磨削比严重下降。超声切削时的磨粒−工件接触比在0.6~0.8,磨粒主要处于断续切削过程,其最大切削宽度比普通切削时的增加2.7倍,且磨粒受到的最大瞬时切削力增加。根据点云信息对磨粒进行逆向建模,并对建立的单颗磨粒切削仿真模型的瞬时切削力进行定量分析。仿真结果显示:超声切削时的最大切向力比普通切削时的增加20%以上,且力的波动幅度超过80%。Abstract: The abrasive wear characteristics of large length to diameter ratio CBN single-pass honing tools during ultrasonic dressing process were studied by single abrasive test with 4Cr13 stainless steel as dressing material. The test results show that the average cutting force during ultrasonic cutting is reduced by 60%~80% compared to that during ordinary cutting. However, the abrasives break in a short time and the grinding ratio is seriously reduced. The abrasive-workpiece contact ratio during ultrasonic cutting is mainly between 0.6 and 0.8, and the abrasives are mainly in the intermittent cutting process. Moreover, the maximum cutting width during ultrasonic cutting increase by 2.7 times compared with that during ordinary cutting, leading to an increase in the maximum cutting force on the abrasives. According to the point cloud information, the abrasive was modeled inversely, and a single abrasive cutting simulation model was established to quantitatively analyze the maximum cutting force. The simulation results show that, compared with that during ordinary cutting, the maximum cutting force during ultrasonic cutting is more than 20% higher, and the fluctuation of cutting force is more than 80%.
-
Key words:
- single abrasive cutting /
- abrasive wear /
- ultrasonic /
- cutting force.
-
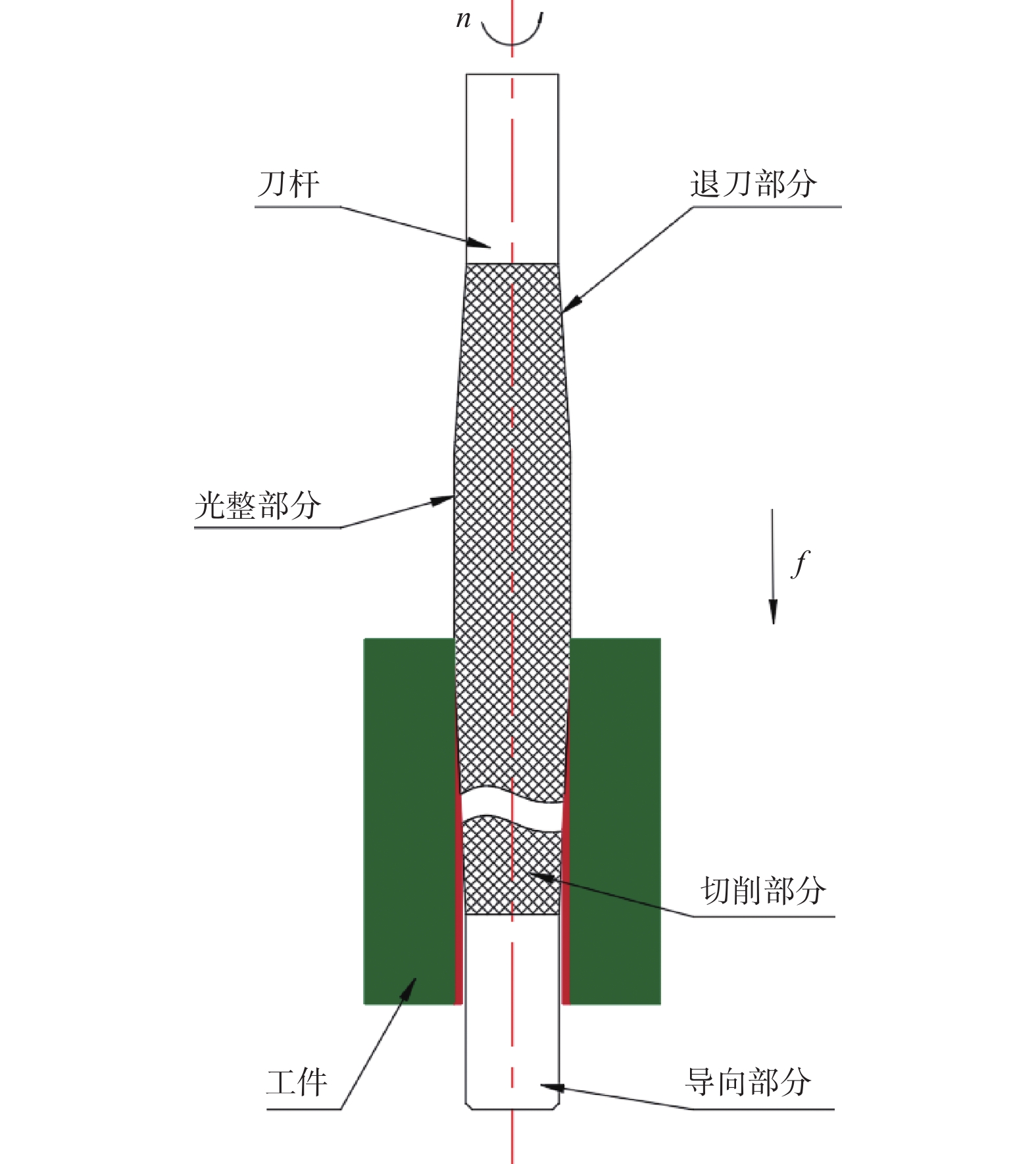
表 1 试验参数
Table 1. Test parameters
参数 取值 CBN磨粒基本颗粒尺寸 D / μm 400~425 主轴转速 n / (r·min−1) 2 000 轴向进给速度 va / (mm·min−1) 6 切削深度 ap / μm 2 超声振幅 A / μm 4 超声频率 f / kHz 21.5 表 2 材料物理性质
Table 2. Material physical properties
材料 密度 ρ / (kg·m−3) 弹性模量 E / GPa 泊松比 υ CBN 3 480 710 0.20 4Cr13 7 800 200 0.24 表 3 4Cr13的Johnson-Cook模型参数
Table 3. Johnson-Cook model parameters of 4Cr13
参数 取值 屈服应力参数 A1 / MPa 600 硬化系数 B / MPa 221 应变率系数 C 0.023 硬化指数 n1 0.6 温度系数 m 1 -
[1] YANG C, SU H, GAO S, et al. Characterization and life prediction of single-pass honing tool for fuel injection nozzle [J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics,2021,34(4):225-240. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2020.08.008 [2] 陈凯, 杨长勇, 高绍武, 等. 单颗CBN磨粒微切削硬质合金YG8磨损研究 [J]. 机械制造与自动化,2021,50(1):25-28. doi: 10.19344/j.cnki.issn1671-5276.2021.01.007CHEN Kai, YANG Changyong, GAO Shaowu, et al. Study on wear of single CBN grain micro-cutting YG8 cemented carbide [J]. Machine Building and Automation,2021,50(1):25-28. doi: 10.19344/j.cnki.issn1671-5276.2021.01.007 [3] 刘伟, 邓朝晖, 万林林, 等. 单颗金刚石磨粒切削氮化硅陶瓷仿真与试验研究 [J]. 机械工程学报,2015,51(21):191-198. doi: 10.3901/JME.2015.21.191LIU Wei, DENG Zhaohui, WAN Linlin, et al. Simulation and experiment study for silicon nitride cutting with single diamond grain [J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2015,51(21):191-198. doi: 10.3901/JME.2015.21.191 [4] 程强, 梁国星, 郝建宇, 等. 高速磨削Inconel718单颗PCBN磨粒磨损研究 [J]. 机电工程,2020,37(10):1225-1230. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4551.2020.10.017CHEN Qiang, LIANG Guoxing, HAO Jianyu, et al. Wear study of single PCBN abrasive in high speed grinding Inconel718 [J]. Journal of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering,2020,37(10):1225-1230. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4551.2020.10.017 [5] 余剑武, 肖清, 罗红, 等. 单颗立方氮化硼磨料磨损过程试验研究与分析 [J]. 兵器材料科学与工程,2017,40(3):16-20. doi: 10.14024/j.cnki.1004-244x.20170503.001YU Jianwu, XIAO Qing, LUO Hong, et al. Experimental research and analysis on CBN wear process based on single abrasive grinding [J]. Ordnance Material Science and Engineering,2017,40(3):16-20. doi: 10.14024/j.cnki.1004-244x.20170503.001 [6] LI B, YIN J, ZHU Y, et al. Grain wear evolution of cubic boron nitride abrasives during single grain grinding of powder metallurgy superalloy FGH96 [J]. Ceramics International,2021,47(2):2508-2516. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.09.094 [7] WANG J, YU T, DING W, et al. Wear evolution and stress distribution of single CBN super abrasive grain in high-speed grinding [J]. Precision Engineering,2018,54:70-80. [8] 王艳凤. 超声辅助单颗磨粒高速磨削试验研究 [D]. 焦作: 河南理工大学, 2015.WANG Yanfeng. The experimental study on high speed grinding of the single grain with ultrasonic-assisted [D]. Jiaozuo: Henan Polytechnic University, 2015. [9] 向道辉, 周直昆, 刘中云, 等. 超声辅助磨削球墨铸铁表面形貌及磨粒磨损研究 [J]. 河南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2018,37(3):86-92. doi: 10.16186/j.cnki.1673-9787.2018.03.12XIANG Daohui, ZHOU Zhikun, LIU Zhongyun, et al. Study on nodular cast iron surface topography and abrasive wear in ultrasonic vibration assisted grinding [J]. Journal of Henan Polytechnic University (Natural Science),2018,37(3):86-92. doi: 10.16186/j.cnki.1673-9787.2018.03.12 [10] ZHENG F, KANG R, DONG Z, et al. A theoretical and experimental investigation on ultrasonic assisted grinding from the single-grain aspect [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences,2018,148:667-675. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2018.09.026 [11] 刘伟, 刘仁通, 邓朝晖, 等. 单颗磨粒磨削仿真研究进展 [J]. 宇航材料工艺,2018,48(4):1-8. doi: 10.12044/j.issn.1007-2330.2018.04.001LIU Wei, LIU Rentong, DENG Zhaohui, et al. Research progress on single abrasive grain grinding simulation [J]. Aerospace Materials and Technology,2018,48(4):1-8. doi: 10.12044/j.issn.1007-2330.2018.04.001 [12] BERGS T, OHLERT M, PRINZ S, et al. Modeling of the fracture behavior of CBN grains during single grain dressing using FEM [J]. Procedia CIRP,2020,93:1514-1519. doi: 10.1016/j.procir.2020.03.021 [13] 马国峰. 超声辅助单颗粒磨削力及去除机理研究 [D]. 焦作: 河南理工大学, 2016.MA Guofeng. Research on grinding force and removal mechanism of single grain in ultrasonic vibration assisted grinding [D]. Jiaozuo: Henan Polytechnic University, 2016. [14] 陈日曜. 金属切削原理 [M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2002.CHEN Riyao. Metal cutting principle [M]. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2002. [15] CHANDRA N, RAHMAN M. Effect of machining parameters in ultrasonic vibration cutting [J]. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture,2008,48(9):965-974. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2008.01.013 [16] ZHANG L, LI P, TANG S, et al. Mechanical behaviors analysis and Johnson-Cook model establishment of 4Cr13 stainless steel [J]. Key Engineering Materials, 2014, 2750. -





 下载:
下载:




















 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS
