Abrasive flow finishing characteristics of internal cooling channel of turbine blade
-
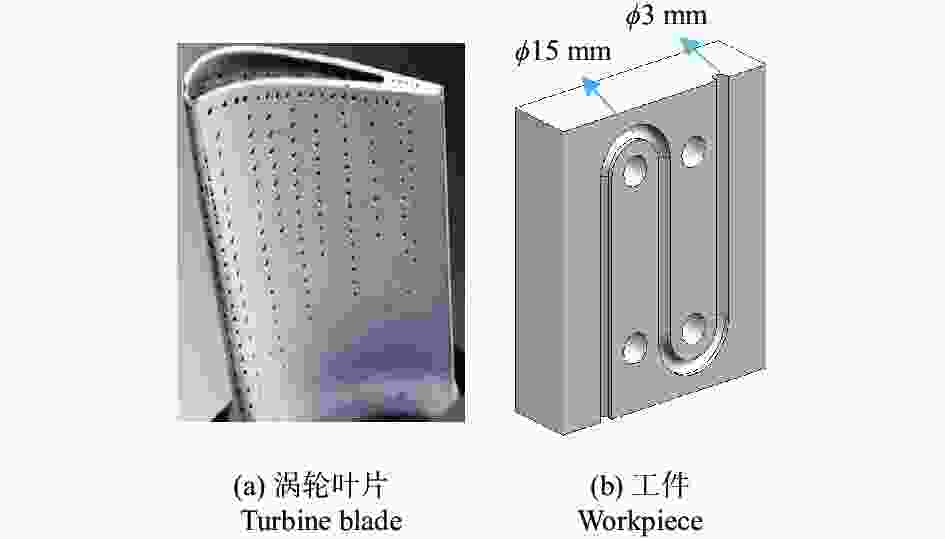
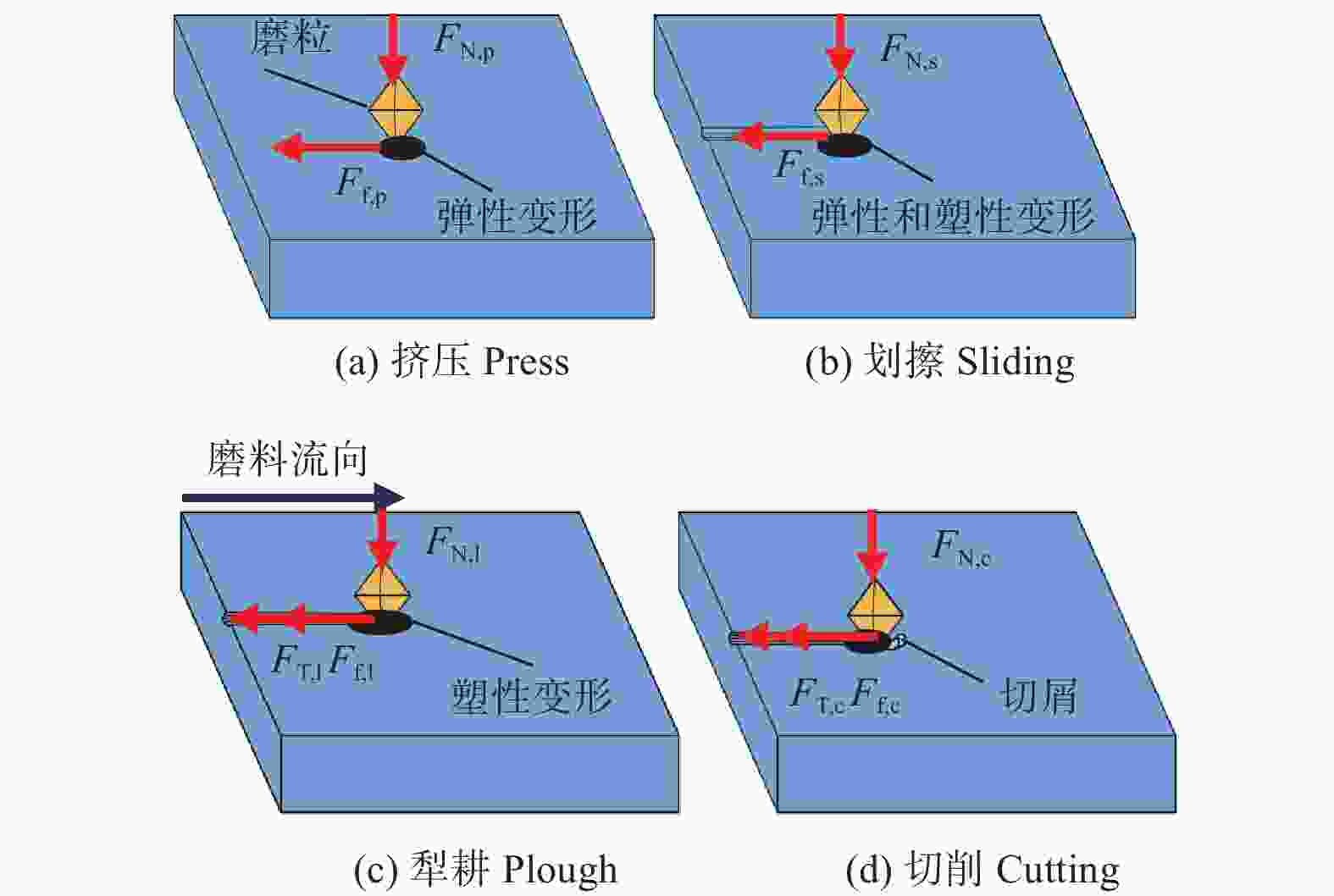
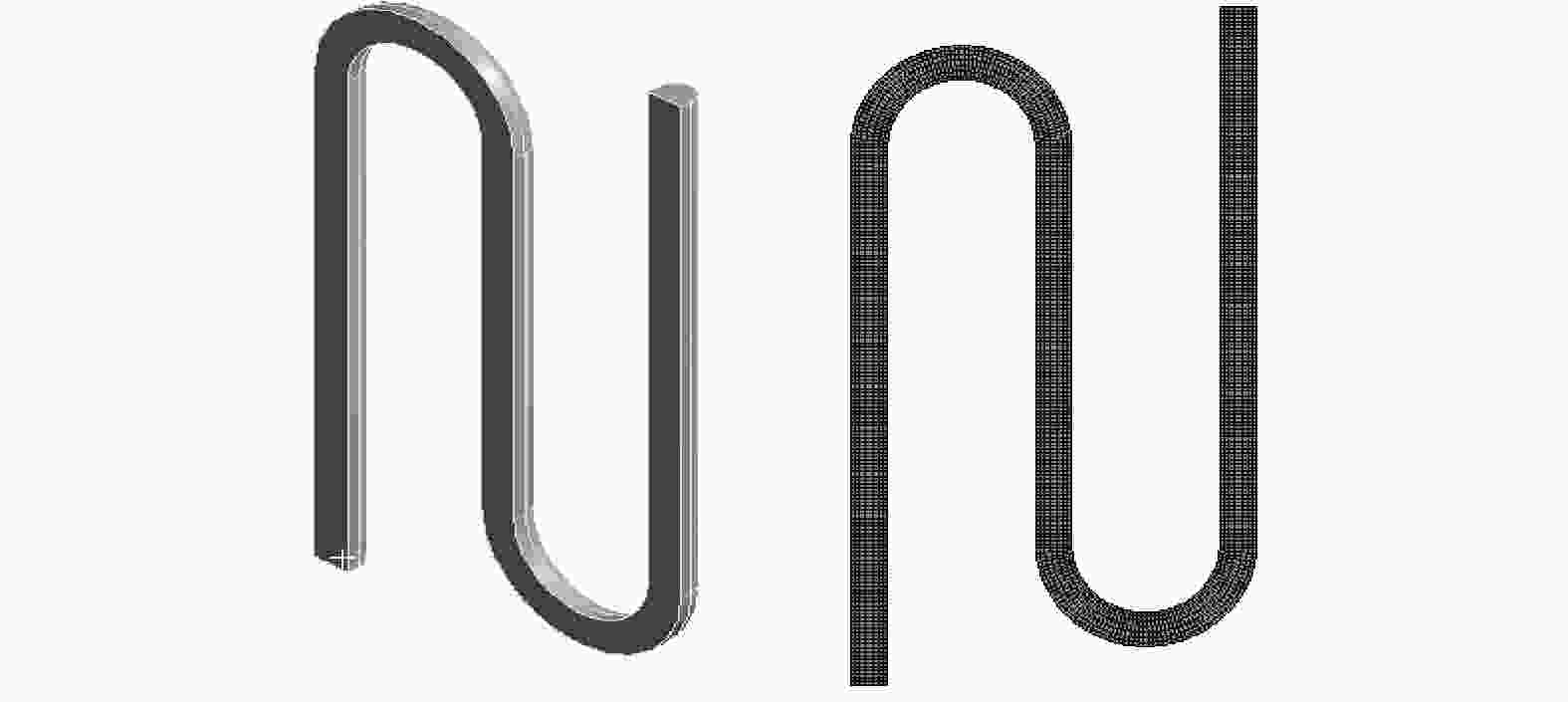
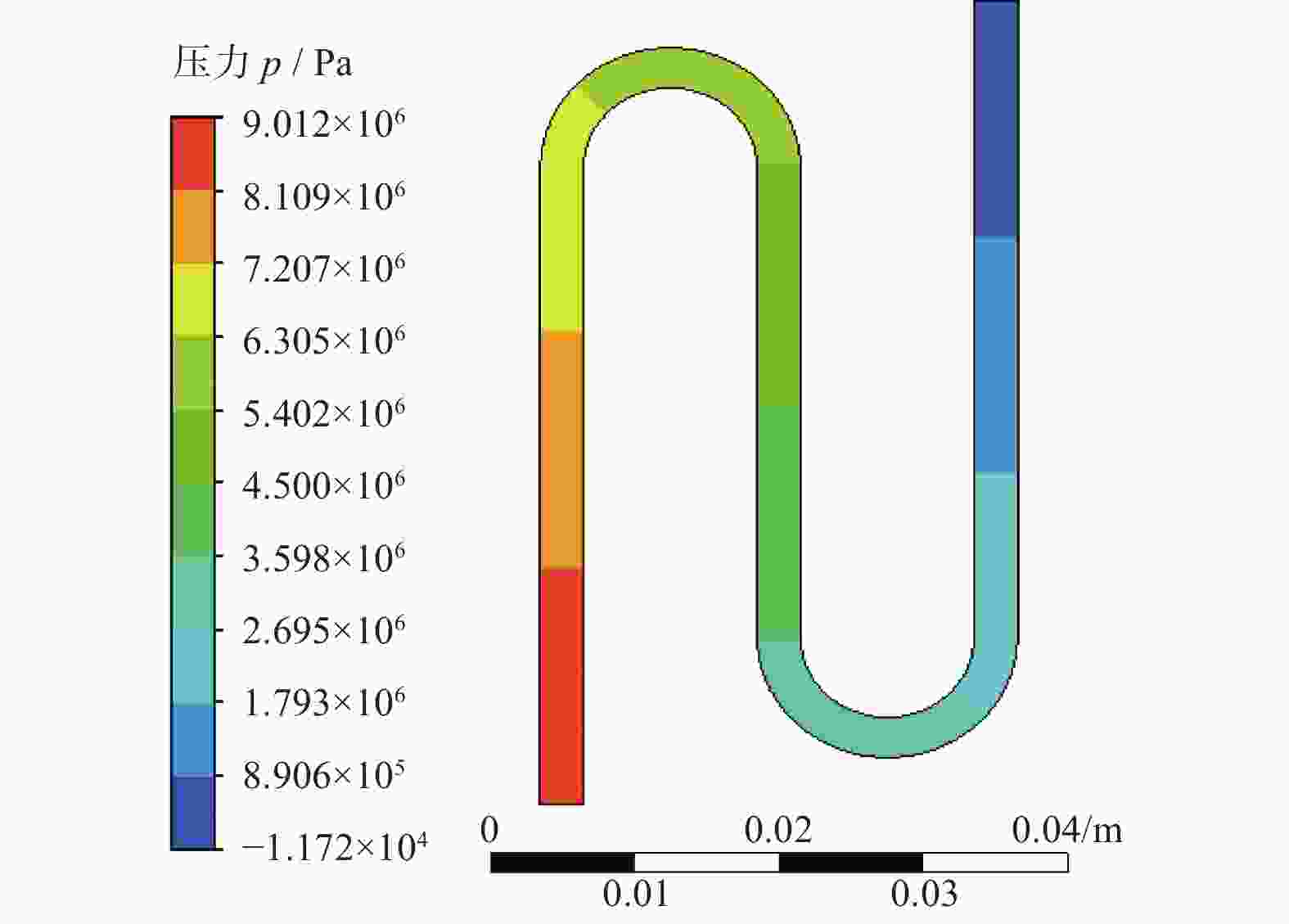
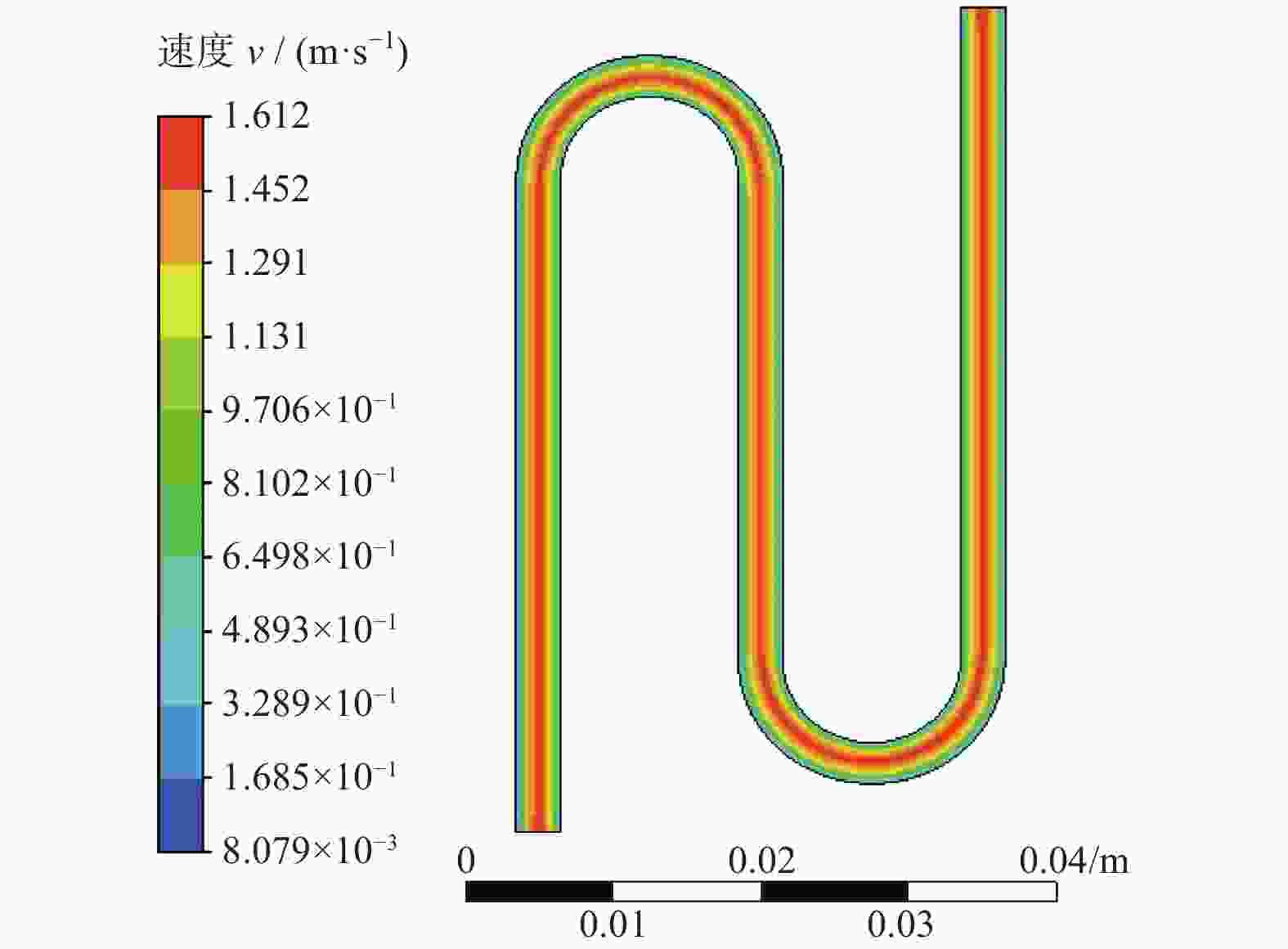
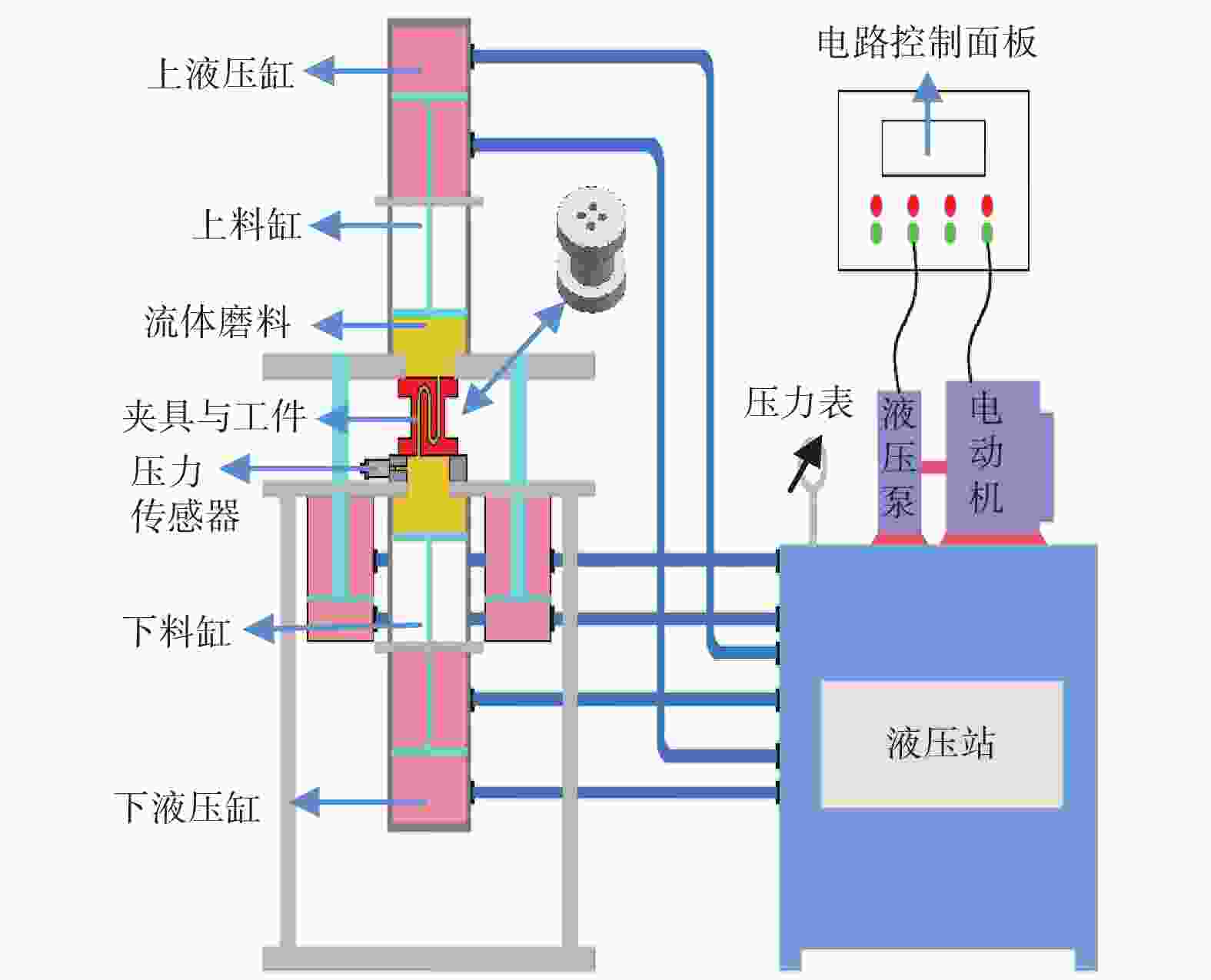
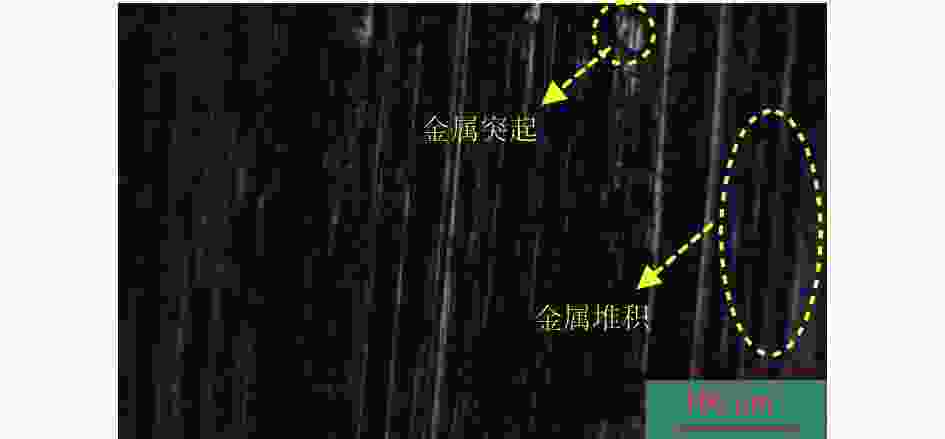
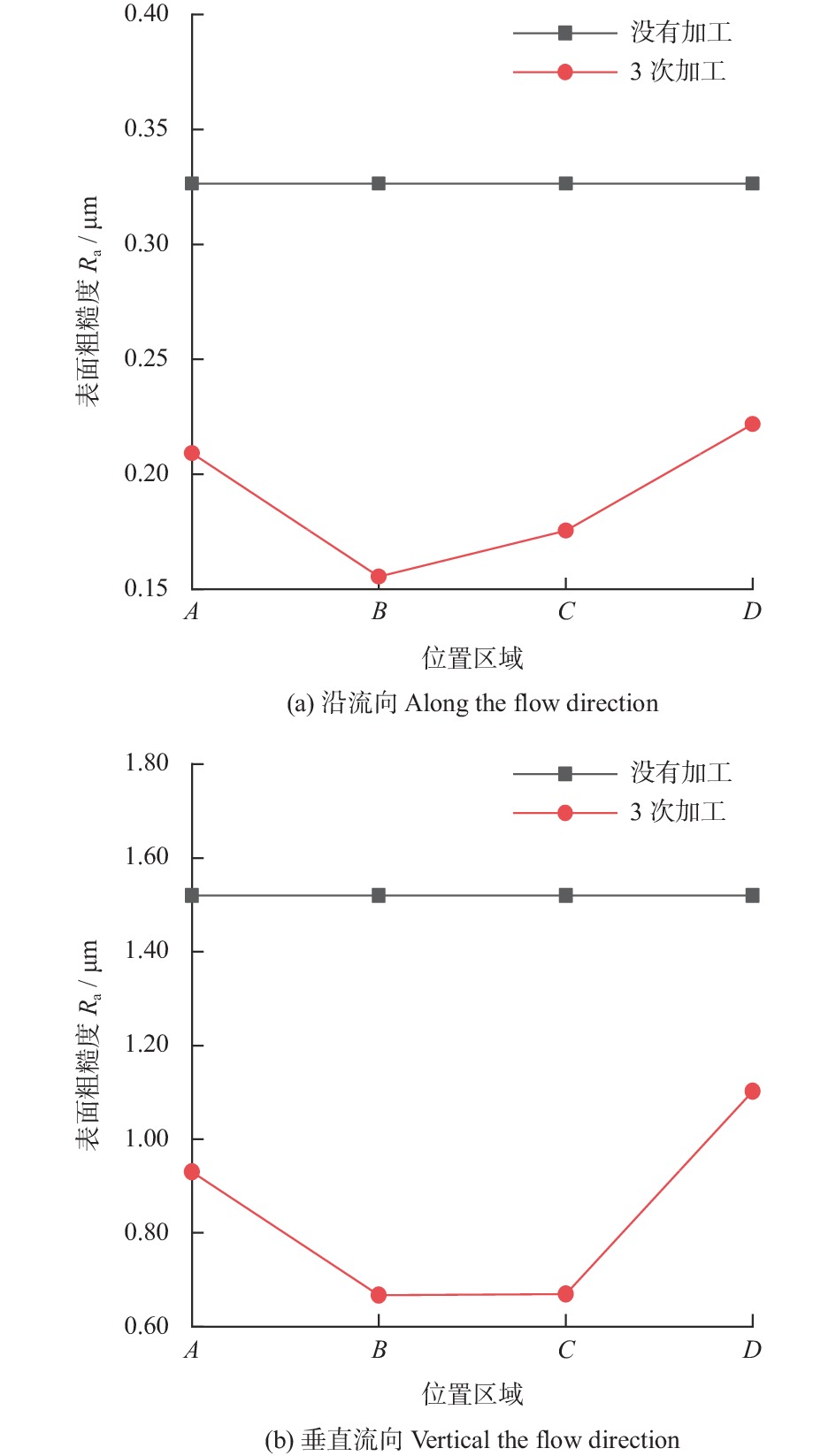
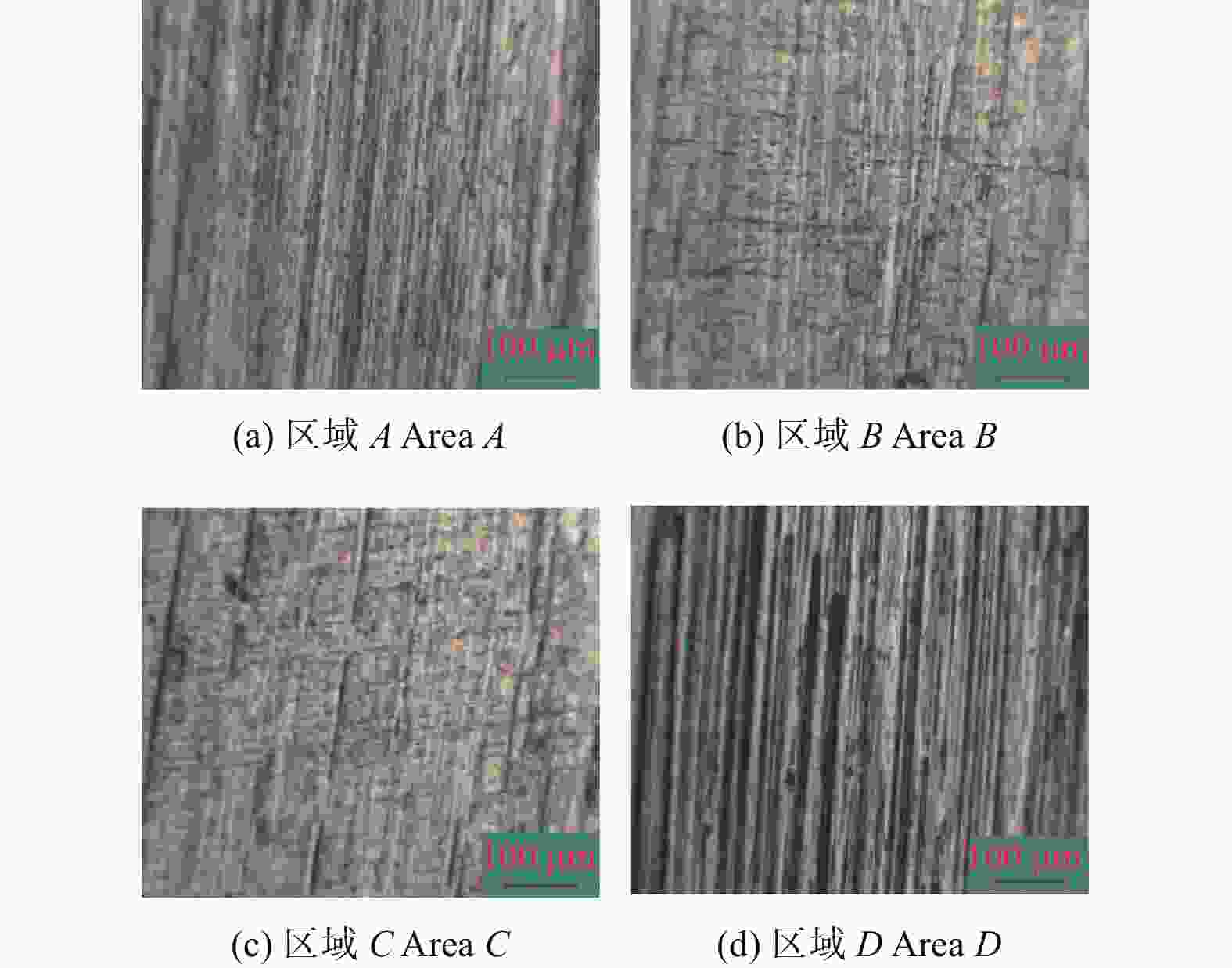
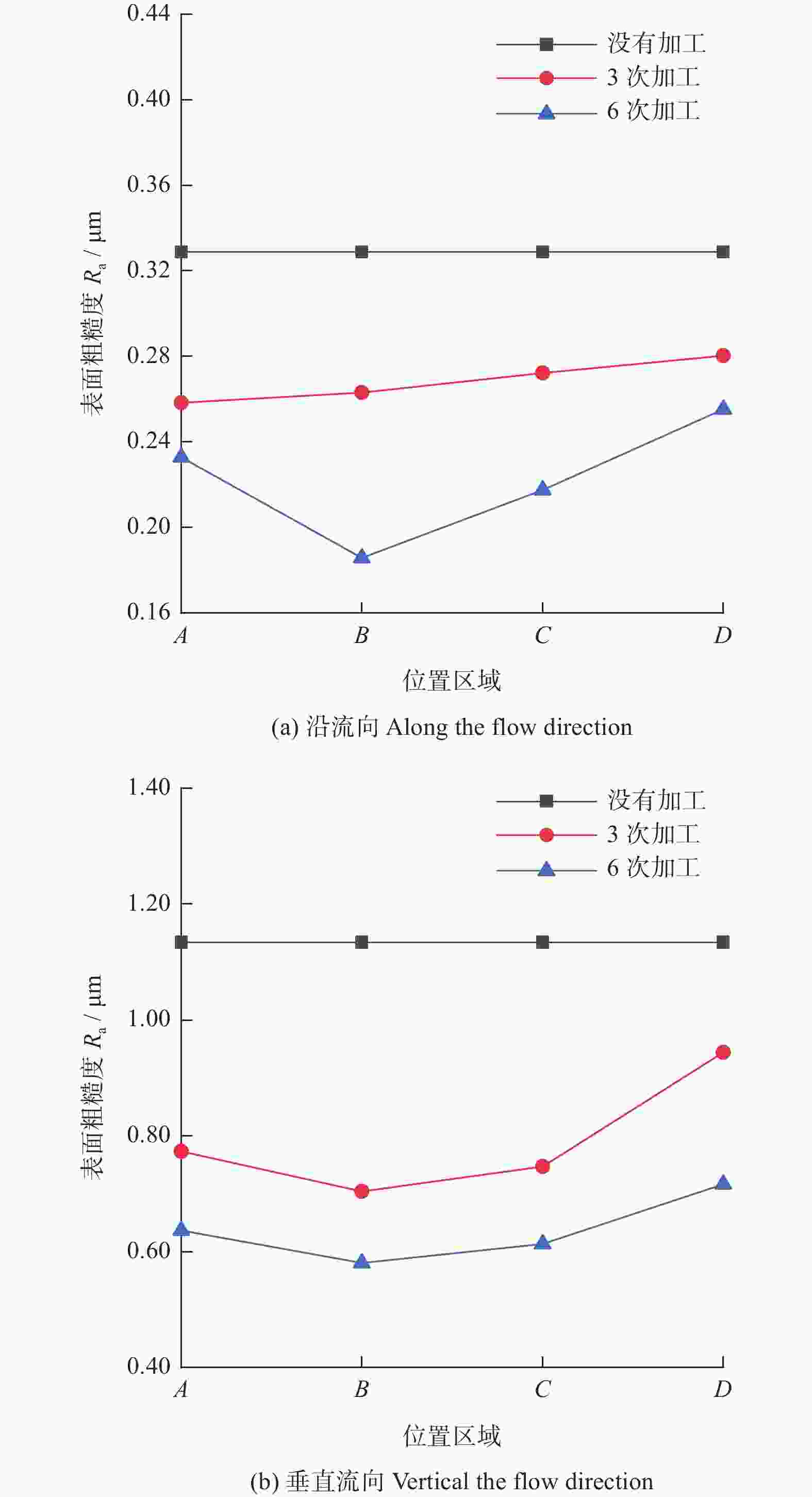
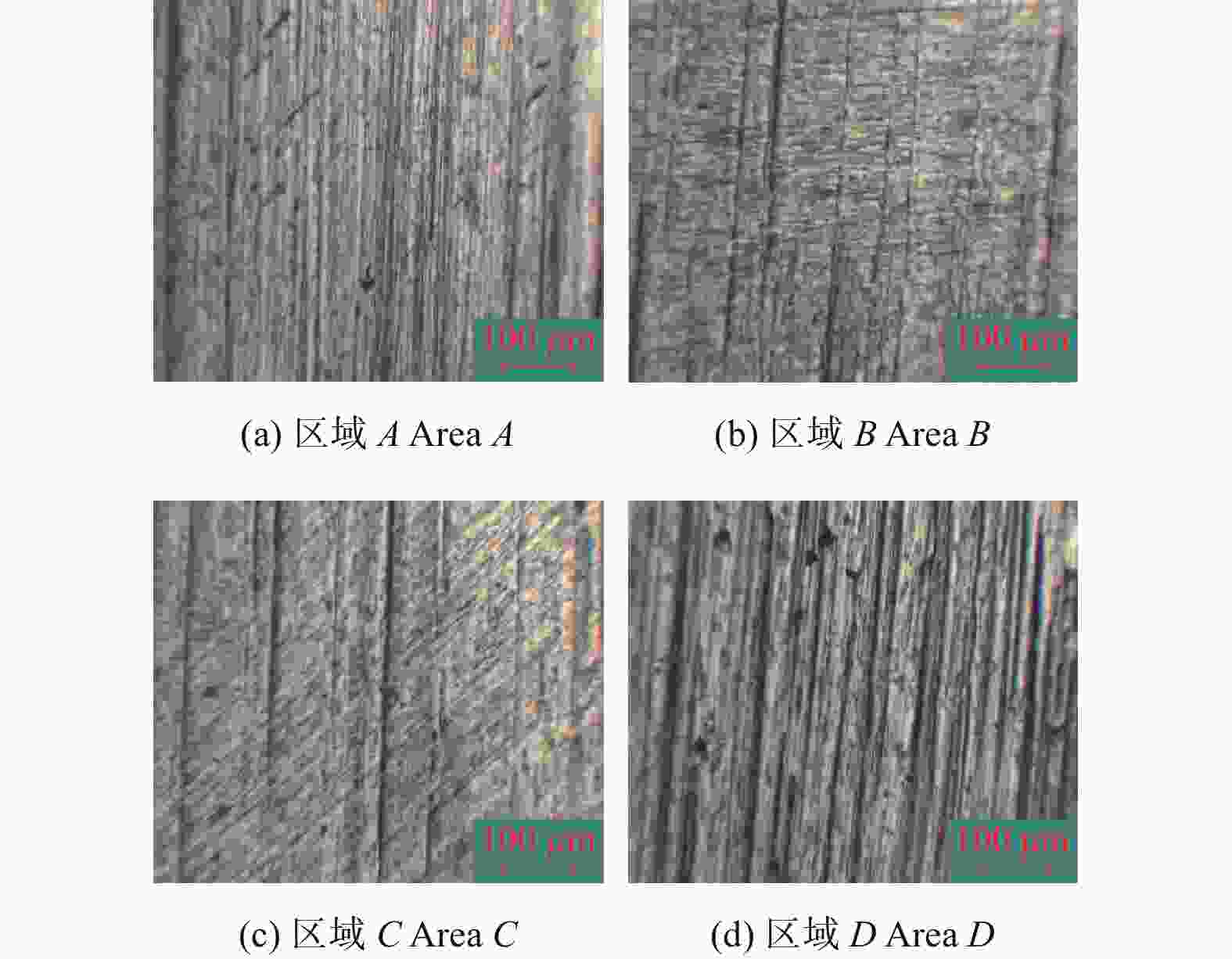
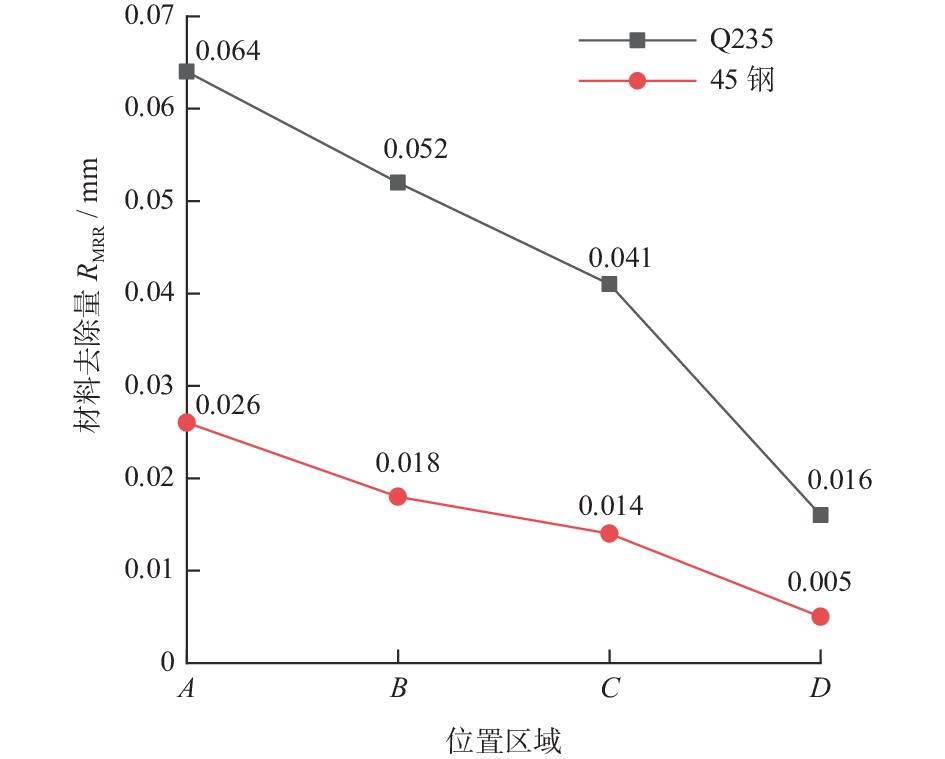
摘要: 航空涡轮叶片内部的多冷却通道多采用消失模铸造等方法制造,其表面粗糙度较高,冷却效率低,内部流道截面小且呈S形弯曲狭长分布,不容易抛光。用Polyflow软件对叶片内冷通道进行仿真,研究其内部压力场、速度场的变化情况。在工件的4个典型区域进行S形内流道加工试验,研究表面粗糙度与材料去除量的变化规律。结果表明:经仿真,压力下降的幅度沿流动方向逐渐变小,速度由通道中心向壁面逐渐减小;相同试验条件下,S形流道转弯处的表面粗糙度比直流道处的低;流道内存在沿程压力损失,区域A比区域D的材料去除量大4~5倍。
-
关键词:
- 磨料流加工 /
- 涡轮叶片 /
- S形流道 /
- Polyflow仿真模拟 /
- 内冷通道
Abstract: The internal multi cooling channels of aviation turbine blades, mostly processed by lost foam casting, have high surface roughness, low cooling efficiency, small internal channel section and S-shaped bending and narrow distribution, and are not easy to polish. The Polyflow software is used to simulate the internal cooling channel of blade, and the changes of internal pressure field and velocity field are studied. The workpiece with S-shaped inner runner was machined and tested to study the variation law of surface roughness and material removal in four typical areas of the workpiece. The results show that the pressure drop decreases along the flow direction and the velocity decreases from the center of the channel to the wall; under the same test conditions, the surface roughness at the turning of S-shaped channel is lower than that at the straight channel; there is pressure loss along the flow path, and the material removal in area A is 4~5 times greater than that in area D. -
表 1 流场网格划分数据
Table 1. Flow field meshing data
类型 最小尺寸a / m 最大尺寸b / m 单元数 节点数 平均网格质量 数值 3.415×10−5 6.831×10-3 27 772 34 650 0.928 67 表 2 试验方案
Table 2. Test scheme
编号 材料 加工次数 磨料粒度尺寸 d / mm 磨粒质量分数 ω / % 1 Q235 3 0.15 30 2 45钢 3 0.15 30 3 45钢 6 0.15 30 -
[1] 周建兴, 陶智, 吴宏, 等. 涡轮叶片尾缘复合冷却通道换热的数值模拟 [J]. 北京航空航天大学学报,2004,30(2):147-151. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5965.2004.02.013ZHOU Jianxing, TAO Zhi, WU Hong, et al. Numerical simulation of heat transfer in turbine blade trailing edge composite cooling passage [J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics,2004,30(2):147-151. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5965.2004.02.013 [2] LI J, QU J, LU H, et al. Effectiveness analysis of abrasive flow polishing S-shaped elbow with side holes based on large eddy simulation [J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2021,115:3887-3906. doi: 10.1007/s00170-021-07384-w [3] LI J, ZHU Z, HU J, et al. Particle collision-based abrasive flow mechanisms in precision machining [J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2020,110(7):1819-1831. [4] 高航, 付有志, 王宣平, 等. 螺旋面磨料流光整加工仿真与试验 [J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版),2016,50(5):920-926. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008973X.2016.05.015GAO Hang, FU Youzhi, WANG Xuanping, et al. Simulation and experiment of helical abrasive streamer finishing [J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science),2016,50(5):920-926. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008973X.2016.05.015 [5] 计时鸣, 葛江勤, 高涛, 等. 基于CFD-DEM耦合的面约束软性磨粒流加工特性研究 [J]. 机械工程学报,2018,54(5):129-141. doi: 10.3901/JME.2018.05.129JI Shiming, GE Jiangqin, GAO Tao, et al. Research on machining characteristics of surface constrained soft abrasive flow based on CFD-DEM coupling [J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2018,54(5):129-141. doi: 10.3901/JME.2018.05.129 [6] WILLIAMS R. A acoustic emission characteristics of abrasive flow machining [J]. Journal of Manufacturing Science and Engineering,1998,120(2):264-271. doi: 10.1115/1.2830123 [7] 穆轩. 航空发动机涡轮叶片气膜孔直径与位置度测量研究 [D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2018.MU Xuan. Research on diameter and position measurement of aero-engine turbine blade film holes [D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2018. [8] 李俊烨, 朱旭, 杨兆军, 等. 固液两相磨料流的微小孔精密研抛行为 [J]. 吉林大学学报,2020,50(3):903-913.LI Junye, ZHU Xu, YANG Zhaojun, et al. Fine-hole precision polishing behavior of solid-liquid two-phase abrasive flow [J]. Journal of Jilin University,2020,50(3):903-913. [9] 张宇超, 董志国, 雷鸿博, 等. 超声振动辅助软性磨料流喷孔光整加工研究 [J]. 组合机床与自动化加工技术,2021(7):165-169. doi: 10.13462/j.cnki.mmtamt.2021.07.038ZHANG Yuchao, DONG Zhiguo, LEI Hongbo, et al. Research on soft abrasive jet finishing assisted by ultrasonic vibration [J]. Modular Machine Tool & Automatic Manufacturing Technique,2021(7):165-169. doi: 10.13462/j.cnki.mmtamt.2021.07.038 [10] 计时鸣, 李琛, 谭大鹏, 等. 基于Preston方程的软性磨粒流加工特性 [J]. 机械工程学报,2011,47(17):156-163. doi: 10.3901/JME.2011.17.156JI Shiming, LI Chen, TAN Dapeng, et al. Machining characteristics of soft abrasive flow based on Preston equation [J]. Journal of mechanical engineering,2011,47(17):156-163. doi: 10.3901/JME.2011.17.156 [11] FU Y, GAO H, YAN Q, et al. An efficient approach to improving the finishing properties of abrasive flow machining with the analyses of initial surface texture of workpiece [J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2020,107(3):2417-2432. [12] 汤勇, 陈澄洲, 张发英. 磨料流加工压力特性对加工表面粗糙度的影响 [J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),1997,25(5):25-28.TANG Yong, CHEN Chengzhou, ZHANG Faying. Influence of abrasive flow machining pressure characteristics on machined surface roughness [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),1997,25(5):25-28. -




 下载:
下载:



 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS
