Influence factors of soluble crystal properties on cutting quality of biological bone materials
-
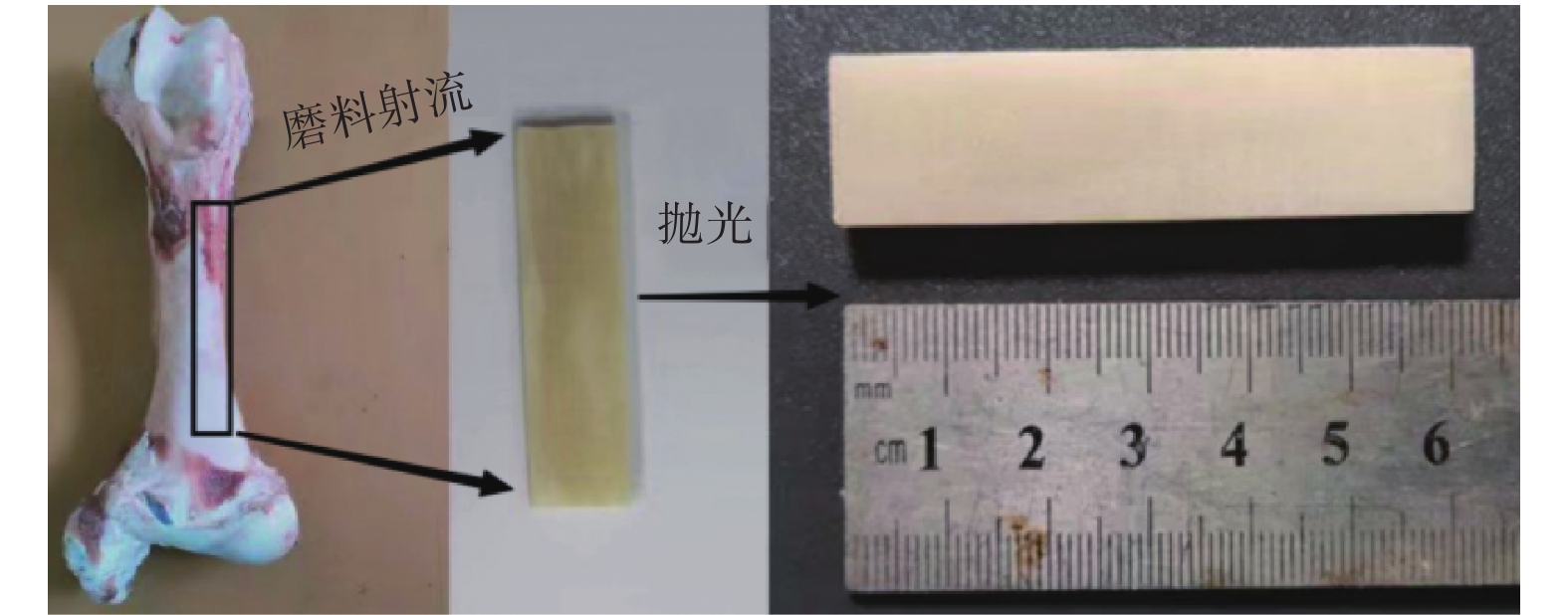
摘要: 为了弥补传统磨料水射流可能造成的磨料残存不利于组织愈合且存在毒害影响的不足,采用具有生物相容性的氯化钠、蔗糖和木糖醇3种可溶性晶体颗粒为磨料,通过改变横移速度和靶距对牛股骨进行切削,测量其表面粗糙度和切削深度,探究可溶性晶体性质对生物骨切削质量的影响。结果表明:氯化钠、蔗糖和木糖醇3种可溶性晶体颗粒作为磨料掺入射流束中,能够明显改善纯水射流切削生物骨材料的质量;可溶性晶体的密度、硬度、溶解性和晶体结构等性质对切削质量均有影响,在能够完全切透骨样的情况下,其中的密度差异表现最明显,密度小的可溶性晶体加工得到的骨样粗糙度更小;在不能够完全切透骨样的情况下,其中的溶解性差异表现最明显,溶解速度慢的晶体加工得到的骨样切削深度更大。在试验设计的参数条件下,3种可溶性晶体射流都能够完全实现生物骨材料的稳定切割,用密度最小的木糖醇颗粒为磨料切削时,在压力为280 MPa,横移速度为10 mm/min,靶距为1 mm时,表面粗糙度值Ra最小,Ra值为3.19 μm;用溶解速度慢的蔗糖为磨料,在压力为280 MPa,横移速度为 10 mm/min,靶距为1 mm时,最大切削深度值为47.15 mm。Abstract: The traditional abrasive water jet may cause abrasive, which is unfavorable to the remnant healing. There also exists the shortage of the deleterious effects of sodium chloride with biocompatibility. In order to solves the problems, three soluble sucrose and xylitol crystal particles are used as abrasives. This study, by changing the traverse speed and target distance to cut cattle femur, measures the surface roughness and cutting depth to explore the effect of soluble crystal properties on the cutting quality of biological bone. The results show that adding sodium chloride, sucrose and xylitol into the jet beam as abrasive can obviously improve the lack of pure water jet cutting biological bone materials with high quality. The density, hardness, solubility and crystal structure of soluble crystals all have an effect on the cutting quality, among which the difference of density is the most obvious in the case of complete cutting of transvious crystal. The roughness of bone is smaller when the soluble crystal with low density is processed. In the case of not being able to completely cut the transvious bone, the difference in solubility was the most obvious. The cutting depth of the bone is greater when the crystal with slow dissolution rate is processed. Under the parameters designed in the experiment, the three kinds of soluble crystal jets can fully realize the stable cutting of biological bone materials. Using the xylitol particles with the lowest density as abrasive, the minimum surface roughness Ra is 3.19 μm when the pressure is 280 MPa, the transverse velocity is 10 mm/min and the target distance is 1 mm. The maximum cutting depth of 47.15 mm is obtained when the pressure is 280 MPa, the transverse velocity is 10 mm/min and the target distance is 1 mm.
-
Key words:
- abrasive water jet /
- soluble crystal /
- cutting quality /
- bone cutting /
- crystal property
-
表 1 3种可溶性晶体的物化性质
Table 1. Physical and chemical properties of three soluble crystals
名称 晶体类型 晶体结构 密度 ρ /($ \mathrm{g}·{\mathrm{c}\mathrm{m}}^{-3} $) 氯化钠 离子晶体 立方体 2.165 蔗糖 分子晶体 单斜体 1.770 木糖醇 分子晶体 斜方体 1.529 表 2 试验参数
Table 2. Test parameters
项目 参数或取值 磨料类型 氯化钠、蔗糖、木糖醇 切割材料 牛股骨 横移速度 vn /(mm·min−1) 10,30,50 靶距 H / mm 1,3,5 射流压力 p / MPa 280 喷嘴角度 $ \alpha $ /(°) 90 -
[1] 廖志荣. 骨材料切削加工及一种新型刀具研究 [D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2017.LIAO Zhirong. Research on bone material cutting and a new tool [D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2017. [2] 王成勇, 陈志桦, 陈华伟, 等. 生物骨材料切除理论研究综述 [J]. 机械工程学报,2021,57(11):2-32. doi: 10.3901/JME.2021.11.002WANG Chengyong, CHEN Zhihua, CHEN Huawei, et al. Review on the theory of biomaterial excision [J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2021,57(11):2-32. doi: 10.3901/JME.2021.11.002 [3] GUPTA V, SINGH R P, PANDEY P M, et al. In vitro comparison of conventional surgical and rotary ultrasonic bone drilling techniques [J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part H: Journal of Engineering in Medicine,2020,234(4):398-411. doi: 10.1177/0954411919898301 [4] YAN L, WANG Q, LI H, et al. Experimental investigation on cutting mechanisms in fixed diamond wire sawing of bone [J]. Precision Engineering,2021,68:319-325. doi: 10.1016/j.precisioneng.2020.12.020 [5] 弓永军. 磨料水射流切割技术研究现状及其发展趋势 [J]. 液压与气动,2016(10):1-5. doi: 10.11832/j.issn.1000-4858.2016.010.001GONG Yongjun. Research status and development trend of abrasive water jet cutting technology [J]. Chinese Hydraulics & Pneumatics,2016(10):1-5. doi: 10.11832/j.issn.1000-4858.2016.010.001 [6] AGARWAL R, SINGH R P, GUPTA V, et al. Influence of cutting force on temperature, microcracks and chip morphology during rotary ultrasonic bone drilling: An in-vitro study [J]. Journal of the Brazilian Society of Mechanical Sciences and Engineering,2022,44(7):1-10. [7] WANG J, SHANMUGAM D K. Cutting meat with bone using an ultrahigh pressure abrasive waterjet [J]. Meat Science,2009,81(4):671-677. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2008.11.010 [8] MCGEOUGH J A. Cutting of food products by ice-particles in a water-jet [J]. Procedia Cirp,2016,42:863-865. doi: 10.1016/j.procir.2016.03.009 [9] EHSAN S, MOHAMMAD A. Investigation of cutting quality and surface roughness in abrasive water jet machining of bone [J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part H: Journal of Engineering in Medicine,2018,232(9):850-861. doi: 10.1177/0954411918790777 [10] SCHWIEGER K, CARRERO V, RENTZSCH R, et al. Abrasive water jet cutting as a new procedure for cutting cancellous bone—in vitro testing in comparison with the oscillating saw [J]. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials,2004,71(2):223-228. [11] 王震, 宋晓菲, 陈彤云. 临床外科手术中骨切削技术的研究现状及进展 [J]. 工程科学学报,2019,41(6):709-718.WANG Zhen, SONG Xiaofei, Chen Tongyun. Research status and progress of bone cutting technology in clinical surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Science,2019,41(6):709-718. [12] 王文魁. 晶体形貌学 [M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 2001.WANG Wenkui. Crystal topography [M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 2001 [13] 李福来, 荆正军, 马少华, 等. 磨料水射流加工材料去除机制及影响因素分析 [J]. 山东化工,2021,50(2):129-132. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-021X.2021.02.046LI Fulai, JING Zhengjun, MA Shaohua, et al. Analysis of material removal mechanism and influencing factors in abrasive water jet machining [J]. Shandong Chemical Industry,2021,50(2):129-132. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-021X.2021.02.046 [14] 冯辉霞. 无机及分析化学 [M]. 武汉: 华中科技大学出版社, 2008.FENG Huixia. Inorganic and analytical chemistry [M]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology Press, 2008. [15] 陈显均, 周文, 徐茂钦. 磨料粒径及形状对磨料水射流切割钛合金表面微观形貌的影响 [J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程,2020,40(2):78-83. doi: 10.13394/j.cnki.jgszz.2020.2.0013CHEN Xianjun, ZHOU Wen, XU Maoqin. Effect of abrasive particle size and shape on the surface micromorphology of titanium alloy cut by abrasive water jet [J]. Diamond & Abrasives Engineering,2020,40(2):78-83. doi: 10.13394/j.cnki.jgszz.2020.2.0013 -





 下载:
下载:








 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS
